🍌 Banana
Important points, botany, varities, pests
- Botanical Name:
Musa paradisica - Family: Musaceae
- Origin: South East Asia
- Also called Apple of paradise/ Kalpathrau (A plant of virtues / Adams fig/ oldest cultivated tropical fruit.
- India (23%) is the largest producer of banana in the world.
- Andra Pradesh produces highest. In Tamil Nadu, banana is specially grown for leaf production.
- Banana is staple food of South Africa.
- Ripe banana fruit contain over 26% of sugar.
- In monthan variety of Banana only Glucose sugar is found.
- Musa acuminate is the source of today’s edible banana.
- Growth of Banana is influenced by temperature.
- It grows well at temperature of
26.5 °C. - Temperature between 20-30 °C is ideal for good plant growth.
- Temperature above 36-38 °C causes scorching effect with increased transpiration.
- It grows well at temperature of
- Fruit type is berry.
- Propagated by suckers/corns.
- Weight of sword suckers generally used:
500 -750 g - Apart from sword sucker (weighing 500-750 g), cut rhizomes called ‘bits’ and ‘peepers’ are also used for propagation.
- In banana commonly found:
Vegetative parthenocarpy. - Genetic classification of Banana was given by Simmond & Shephard.
- Inflorescence of banana is known as
spadix. - Most of cultivated banana are Triploid in nature.
- Diploid banana variety is Lady finger
- AAB, AAA clones are grown under irrigated conditions.
- ABB clones are grown under rainfed conditions [Monthan, Kanthali, Kunnan]
- High uptake nutrient
‘K’among N, P and K. - Banana is a rich source of dietary potassium (K) used in nervous impulses and good source of energy.
- Seedlessness in banana is controlled by spray of 2, 4-D @ 25 PPM
- Poovan, Rasthali, Nendran and Robusta 2.1 X 2.1 (m2)
- Basari, Kulhan, Jawari: 1.8 x 1.8 m2 spacing.
- High density 1.2 x 1.2 m to 1.5 x 1.5 m is common now days.
- Edible part: Starchy Parenchyma.
- Brinjal, cucrbuts should not be grown in Banana orchard because they attract nematodes. Banana initiate flowering 9-12 months after Planting.
- For the ripening of banana, low concentration of ethylene with 15-18 °C in controlled chamber is used. But use of acetylene is not good.
- Artificial ripening is done with chemical calcium carbide.
- Banana fruits can be stored at 13 °C temperature & 85-95% humidity for three weeks.
- Banana is herbaceous, monocotyledonus and monocarpic fruit crop.
- Banana is a calcifuge crop calorific value: 67-137/100 g.
- Banana is moisture loving plant.
Cultural Practices
- Banana
Pseudo-stem- Pseudostem is the part of the plant which looks like trunk. Pseudostem is false stem which is formed by the tightly packed overlapping leaf sheaths.
- Generally green in shiny or wax coated, brown blotched or brown black blotched. 1-8 m tall depends on variety.
- Mettocking: Practice of removing banana pseudostem after harvesting of fruit.
- Desuckering: Descuckering once in 45 days is common practice in Banana cultivation.
- Propping:
- Denavelling: IBPS AFO 2019-20 Removal of
male budafter completion of the female phase.

- Two spray of KH2PO4 at fruit development stage increases the bunch weight.
- In Gujrat and Maharashtra: Furrow method and in Tamil Nadu trench method of planting is followed.
- Trench method is especially followed in wetland system of cultivation.
- For getting maximum yield a minimum of 10-12 leaves are required to be retained on the mother plant.
- Strong wind is a threat for successful banana production.
- For long distance transportation, harvesting is done at 75-80% maturity.
- Post-harvest technology to delay ripening of banana are skin coating with wax & (12% wax emulsion).
- Banana improvement work was started in the year 1949 in Tamil Nadu. Hybridization work— CBRS, Adhuthurai (TN)
- CBRS: Central Banana Research Station
- Maturity: 90-150 days.
- Salt water treatment reduces duration of Banana fruits.
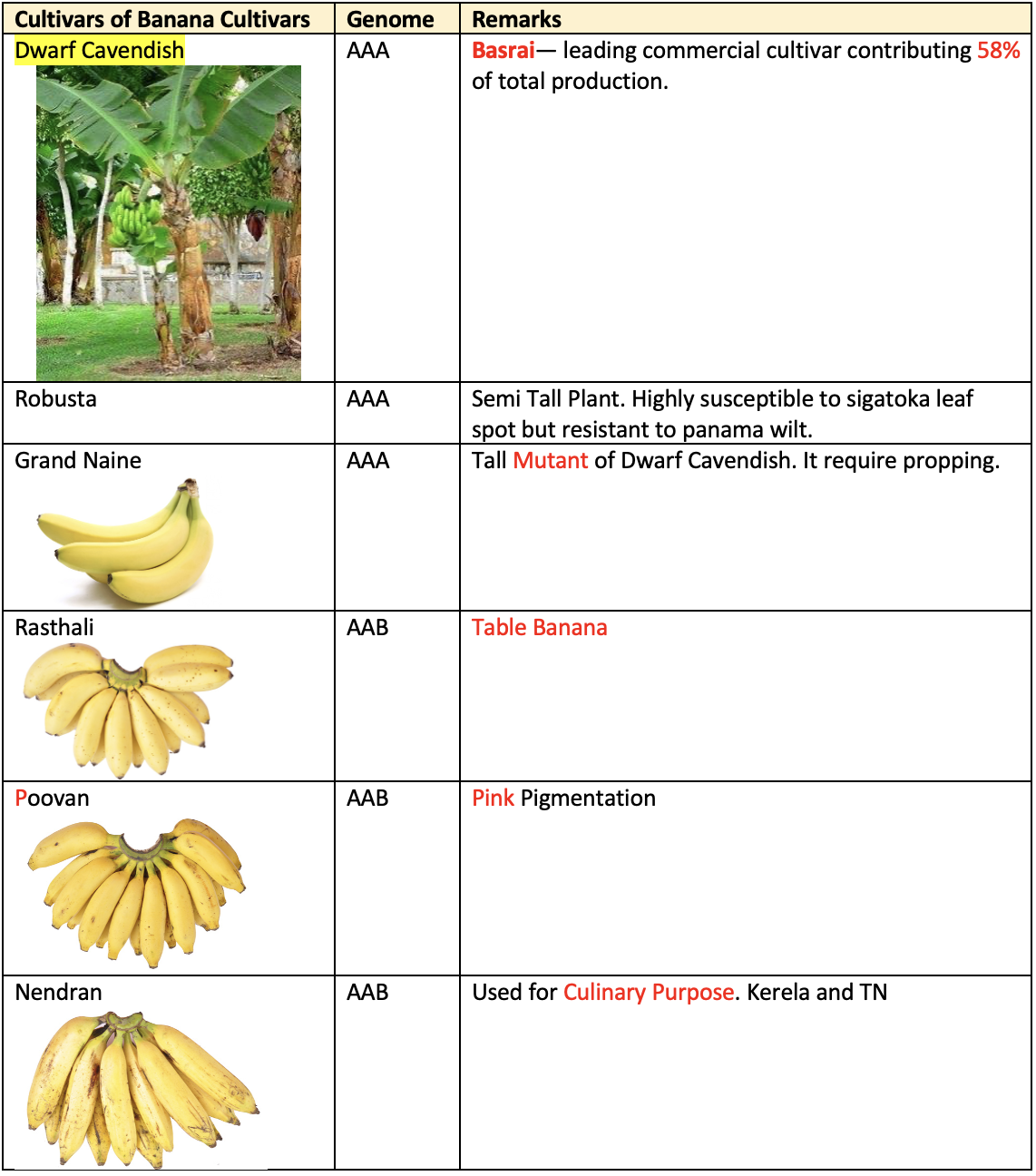
Varieties
- Poovan & Ney poovan are preferred in multistory system.
- Gandevi selection (Hanuman or pardase) from Basrai.
- Poovan (AAB): Rasthali, Amritpani, mortman—choicest table banana (Best) Hard lumps and fruit cracking are the major physiological disorders. Tolerant to many Abiotic & biotic stresses.
- Poovan mvsore (AAB): Pink pigmentation on ventral side of midrib when young, susceptible to banana streak virus, leading cultivar of south India.
- Nendran (AAB): Most prized cooking variety used in Kerala. Good for making Banana chips.
- Hill banana (AAB): Suitable for cultivation on hills, fruits having unique aroma and flavour (taste). Suitable for Jam making.
- Lal velchi (AAA): It is grown for red skin.
- Monthun (ABB): Good for culinary purpose.
- Ney Poovan (AB): diploid variety, it fetches double price than other cultivars. Horizontal bunch orientation.
- Lady finger (AB): diploid banana variety.
Hybrids
- FHIA-1 (Gold Finger) - (AAAB) - Belong to pome group. Resistant to wilt and sigatoka leaf spot.
- Bodies Altafort - (AAAA) - Synthetic hybrid, a result of cross between Gross michel (AAA) x Pisanglin (AA).
- Klue teparod (AABB) - Natural tetraploid.
- CO-1: Kellar Laden x M. balbasiana x Kadali
- Rajapuri: Resistant to cold.
- Nendran: Remain starchy even on ripening.
- Moongli: Mutant of Nendran
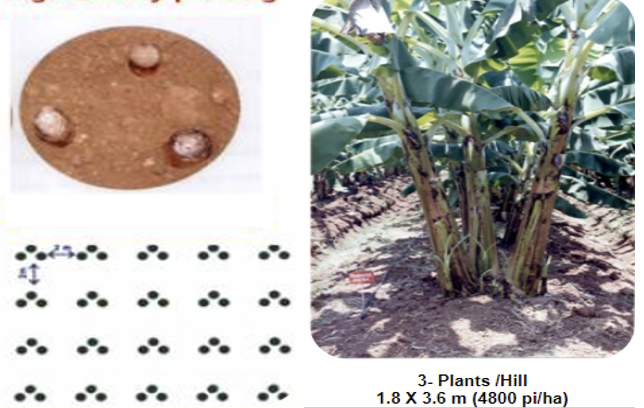
- Sucker treatment: Pralinage - with 40 g of carbofuran 3 G granules per sucker. (The corn is dipped in slurry solution of 4 parts of clay plus 5 parts water and sprinkled with carbofuran to control nematodes.
- High density planting - 3 suckers / pit at a spacing of 1.8 x 3.6 m (4600 plants / ha).

Physiological disorders
Kotta vazhai
In certain pockets of Tamil Nadu, the banana cv. Poovan is manifested with a peculiar development disorder which is characterized by the presence of distinctly conical and ill filled fruits with a prominent central core having many under developed non-viable seedy structures rendering the fruits inedible.

Hard lump
- It is characterized by pinkish brown, firm pulp than the usual soft pulp occurs in cv. Rasthali.
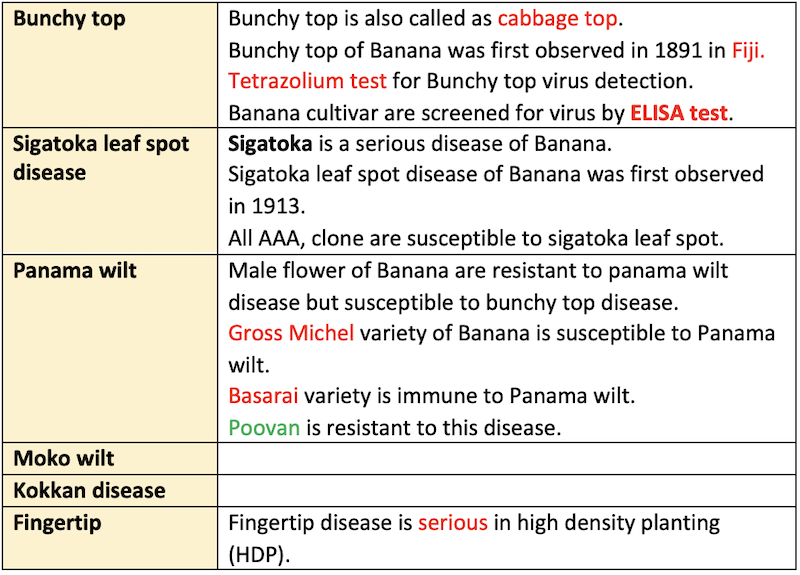
Disease
Insects
- Rhizome/Banana weevil
- Aphids
Yield (t/ha/year)
- Poovan: 40-50
- Monthan: 30-40
- Robusta: 50-60
- Dwarf Cavendish: 50-60
Breeding Problem in Banana
- Major breeding problem in banana is male sterility and parthenocarpy.
Explore More 🔭
- Botanical Name:
Musa paradisica - Family: Musaceae
- Origin: South East Asia
- Also called Apple of paradise/ Kalpathrau (A plant of virtues / Adams fig/ oldest cultivated tropical fruit.
- India (23%) is the largest producer of banana in the world.
- Andra Pradesh produces highest. In Tamil Nadu, banana is specially grown for leaf production.
- Banana is staple food of South Africa.
- Ripe banana fruit contain over 26% of sugar.
- In monthan variety of Banana only Glucose sugar is found.
- Musa acuminate is the source of today’s edible banana.
- Growth of Banana is influenced by temperature.
- It grows well at temperature of
26.5 °C. - Temperature between 20-30 °C is ideal for good plant growth.
- Temperature above 36-38 °C causes scorching effect with increased transpiration.
- It grows well at temperature of
- Fruit type is berry. …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel