🍪 Classification
Fruit morphology, Classification of fruits
Types of fruits
Fruit Morphology
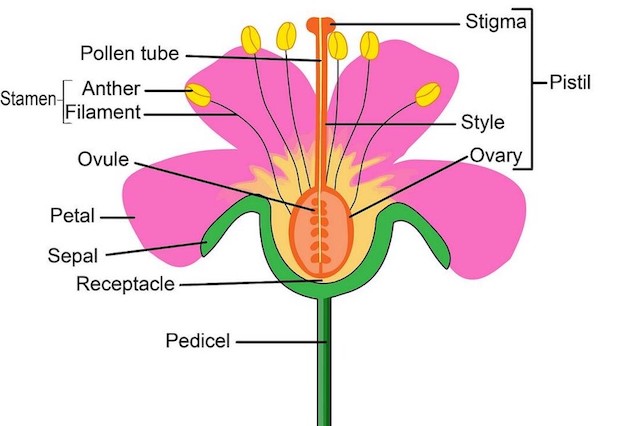
- A fruit consists of pericarp and seeds. Seeds are fertilized and ripened ovules.
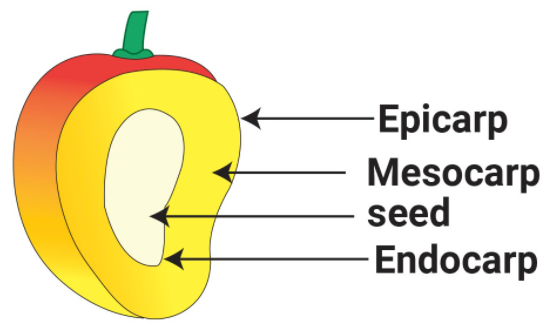
- The pericarp develops from the ovary wall and may be dry or fleshy.
- When fleshy, the pericarp is differentiated into outer epicarp, middle mesocarp and inner endocarp.
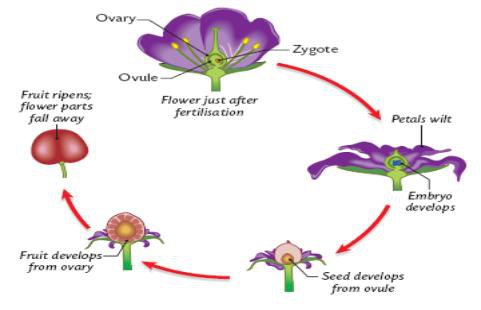
- So, most of the flowers are developed in the following way:
👉🏻 On the basis of the above-mentioned features, fruits are usually classified into 3 main groups:
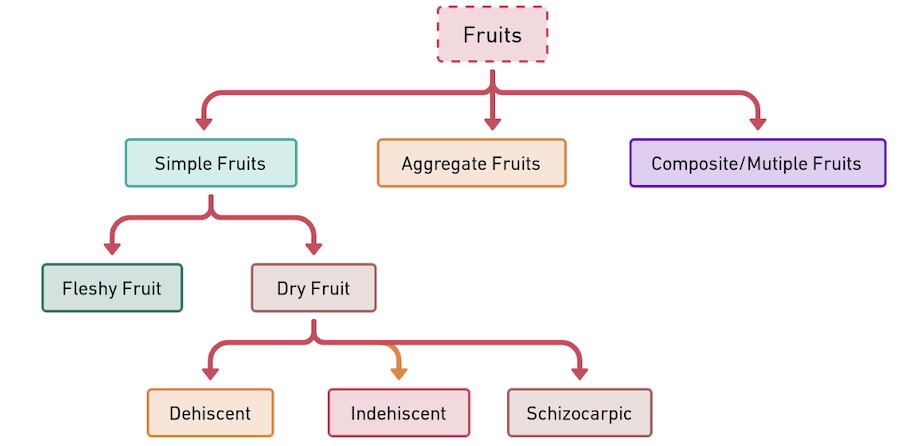
Simple fruits
- When a
single fruitdevelops from asingle ovaryof a single flower, it is called a simple fruit. - Examples:
Banana, ⭐️Grapes, Papaya, Avacado etc. - Simple fruits are of two types:
- Dry Fruits
- Succulent fruits (fleshy fruits)
Dry fruits
- These fruits are not fleshy, and their pericarp (fruit wall) is not distinguished into three layers.
- Dry fruits classification:
- Dehiscent fruits (capsular fruits)
- Characteristic of these fruits is that their pericarp rupture after ripening and the seeds are disseminated.
- Indehiscent fruits (Achenial fruits)
- As their name indicates, pericarp of such fruits does not rupture on ripening and the seeds remain inside.
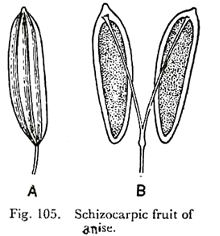
- Schizocarpic fruits (Splitting fruits)
- These fruits fall in between the above-mentioned two categories. Here, the fruit on ripening divides into one-seeded segments or mericarp; but the mericarps remain un-ruptured.
- Dehiscent fruits (capsular fruits)
Succulent fruits (fleshy fruits)
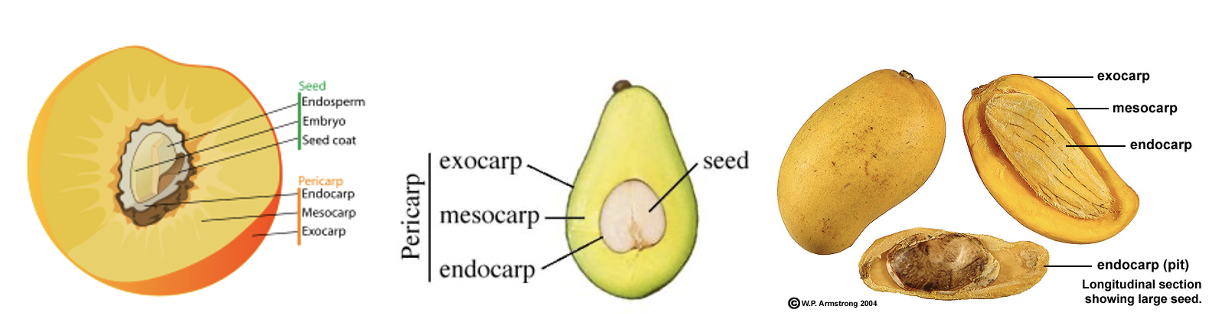
- In these fruits pericarp is distinguished into pericarp, mesocarp and endocarp.
- Mesocarp is fleshy or fibrous.
- These fruits are indehiscent, and seeds are liberated after the decay of the flesh.
- Succulent fruits can be classified into Drupe, Pome and Berrie.
Drupe
- The pericarp or fruit wall is differentiated into thin epicarp (skin), fleshy mesocarp and
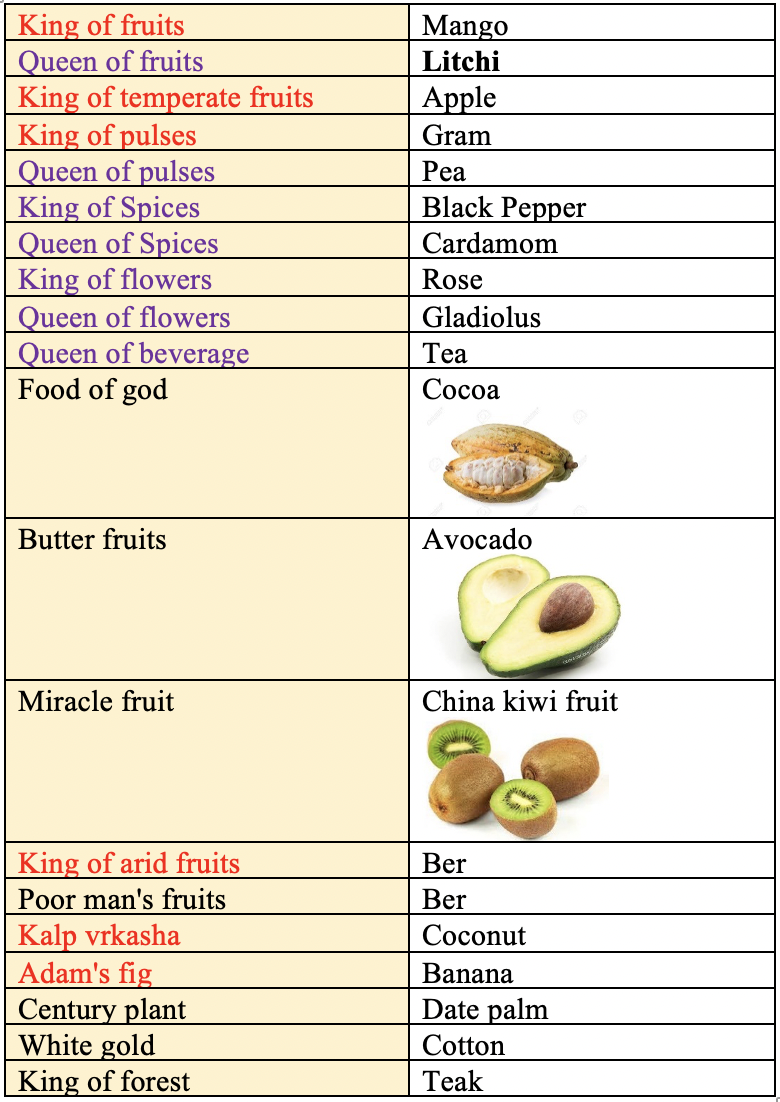
stony endocarp. - Hence it is also called as stone fruit, e.g. Mango, Jamun, Coffee, Coconut, Almond, Plum, Peach etc.
- In mango, mesocarp is juicy and edible.
- In coconut mesocarp is fibrous and edible part is the endosperm. The nuclear endosperm which is suspended within the water of the coconut, develops and forms the edible coconut flesh.
- In almond, epicarp and mesocarp get peeled off and only hard endocarp can be seen in marketed fruits. The edible part is cotyledons.
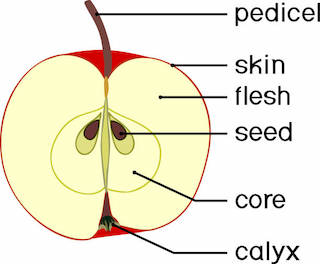
Pome
- It is a simple, fleshy but false fruit as it is surrounded by a fleshy thalamus which is edible while actual fruit lies within.
- E.g. Apple, Pear, Loquat etc.
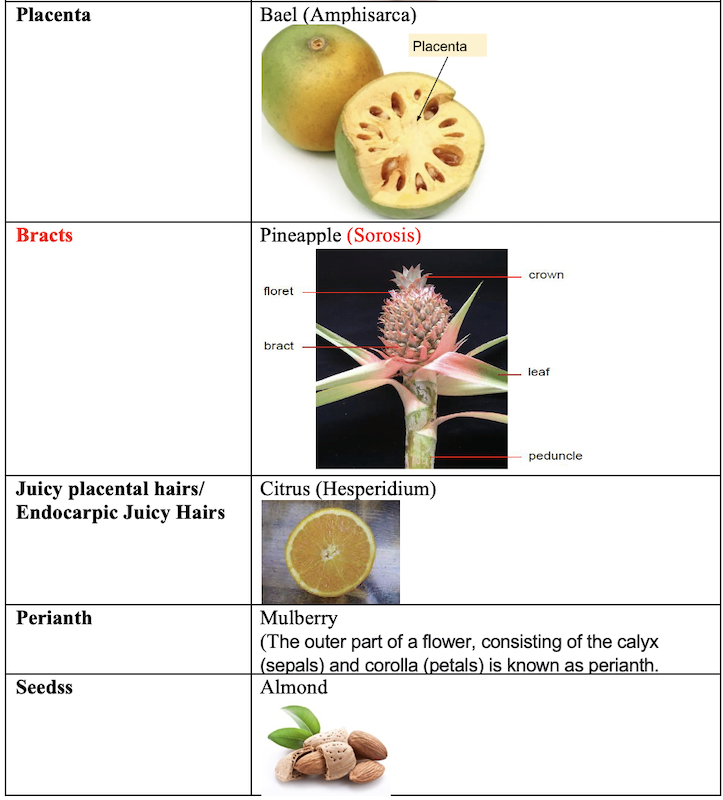
Berry
- Berry is a fleshy fruit in which there is no hard part except the seeds.
- Pericarp may be differentiated into epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp.
- One or other of these layers may form pulp in which seeds are embedded which generally gets detached from the placenta.
- Examples:
Banana,Papaya,Grape,Date Palm,ArecanutandGuava. - The following are some fruits which show variations from the normal Berry:
- Pepo:
Watermelon(Cucurbits) - Hesperidium:
Citrusfruits like oranges and lemons - Amphisarca:
Bael - Balusta:
Pomegranate
- Pepo:
Aggregate fruits
- They develop from the
apocarpous ovariesof a single flower. Thus, from one flower, many fruits develop. - Example: Eteario of berries,
Custard Apple,Raspberry
Multiple or Composite Fruits
- A fruit developing from a
complete inflorescenceis called a multiple or a composite fruit. i.e. many flowers — single fruit. - Examples: Pineapple (
Sorosis) AFO-2021, Fig (Synconus), Jackfruit, Mulberry etc.
Others
- Nuts: Litchi & Cashew
- Capsule: Okra and Aonla
Ediable Part of Fruits
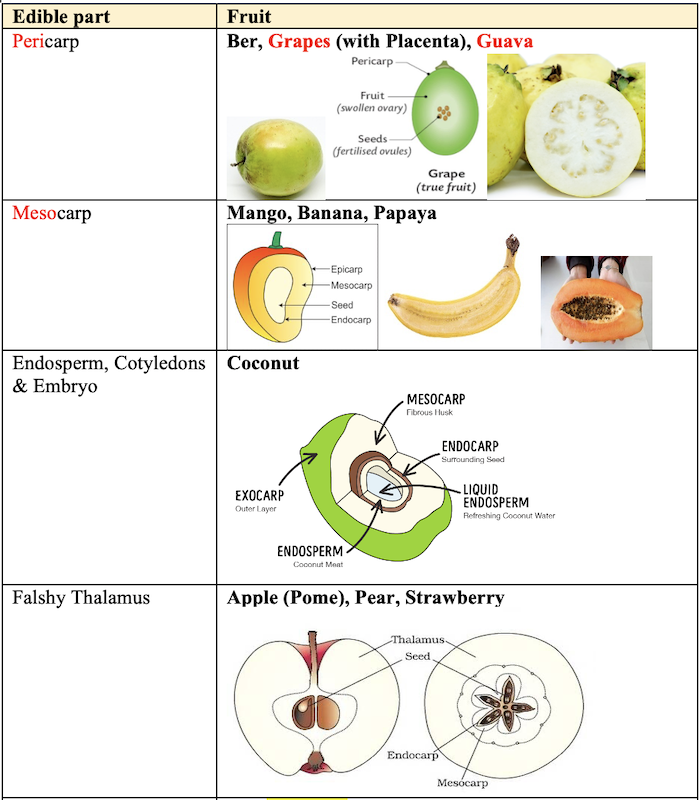

Commonly Known as
Important families of fruit crops
Fruiting Pattern
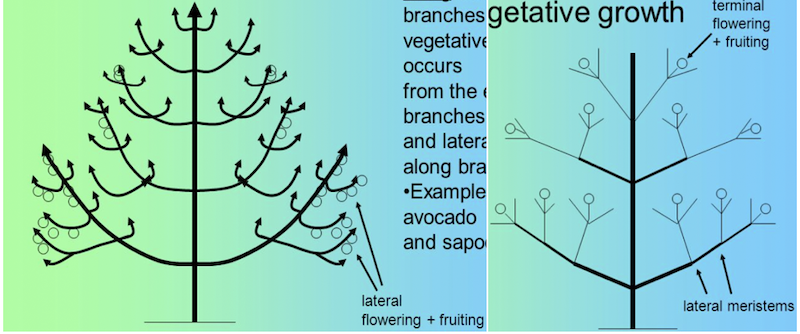
- Lateral bearing cultivars develop fruits on side small branches after three or four years of planting and bear heavily.
- Ex. Mango
- In comparison to lateral bearing, tip bearing plants develop fruit on tips of one year old shoots after six or more years and produces
yield smallerthan lateral bearing cultivars.- Ex. Plum, Pear, Ber, Guava etc.
Types of fruits
Fruit Morphology

- A fruit consists of pericarp and seeds. Seeds are fertilized and ripened ovules.
- The pericarp develops from the ovary wall and may be dry or fleshy.
- When fleshy, the pericarp is differentiated into outer epicarp, middle mesocarp and inner endocarp.

- So, most of the flowers are developed in the following way:

👉🏻 On the basis of the above-mentioned features, fruits are usually classified into 3 main groups:

Simple fruits
- When a
single fruitdevelops from asingle ovaryof a single flower, it is called a simple fruit. - Examples:
Banana, ⭐️Grapes, Papaya, Avacado etc. - Simple fruits are of two types:
- Dry Fruits
- Succulent fruits (fleshy fruits)
Dry fruits
- These fruits are not fleshy, and their pericarp (fruit wall) is not distinguished into …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel