📈 Current Scenario
Production, Area, Leading states and crops in India
Current Status (Final Figures)
- India is
secondlargest producer of horticultural crops. - The scenario of horticulture crops in India has become very encouraging. The percentage share of horticulture GDP to Agriculture has become
32%. (NHB) - Cold Storage:
UP(2368) > GJ (890) > PB (672) in 2017-18.
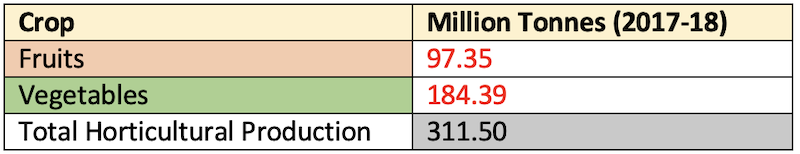
- In 2017-18, the total horticulture production was highest in case of
Uttar Pradesh(392.48 Lakh Tonnes) followed by West Bengal (324.2 Lakh Tonnes). - The total production of fruits is highest in case of
Andhra Pradesh(152.15 Lakh Tonnes) followed by Maharashtra (117.28 Lakh Tonnes). - Apart from nutritional benefits, the production of vegetables improves the economy of a country as these are very good source of income and employment. The contribution of vegetables remains highest (59 – 61%) in horticulture crop productions over the last five years.
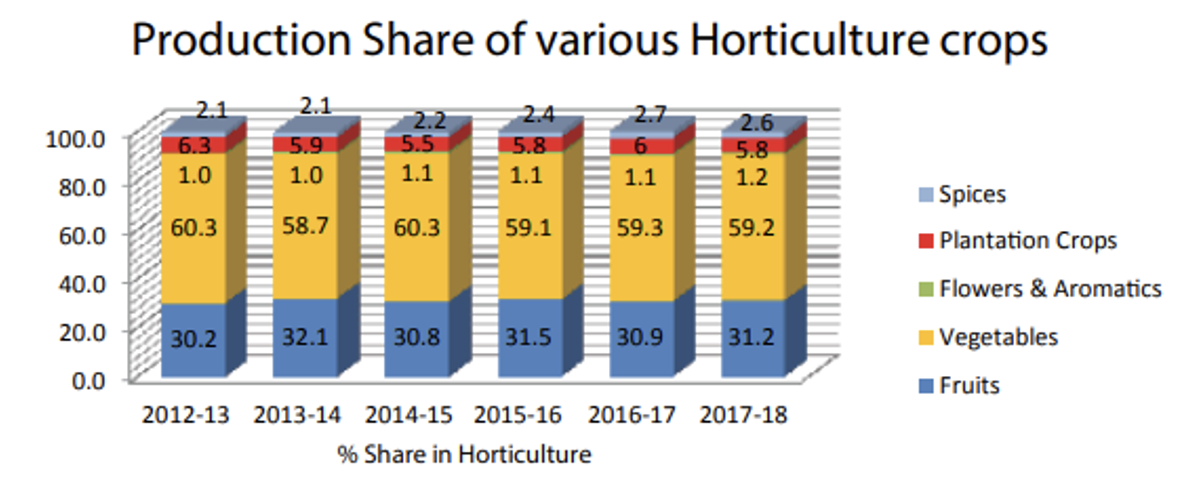
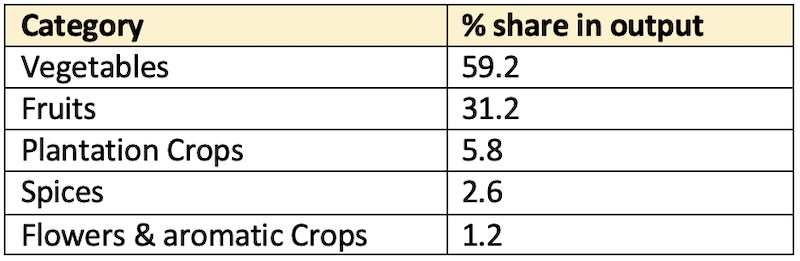
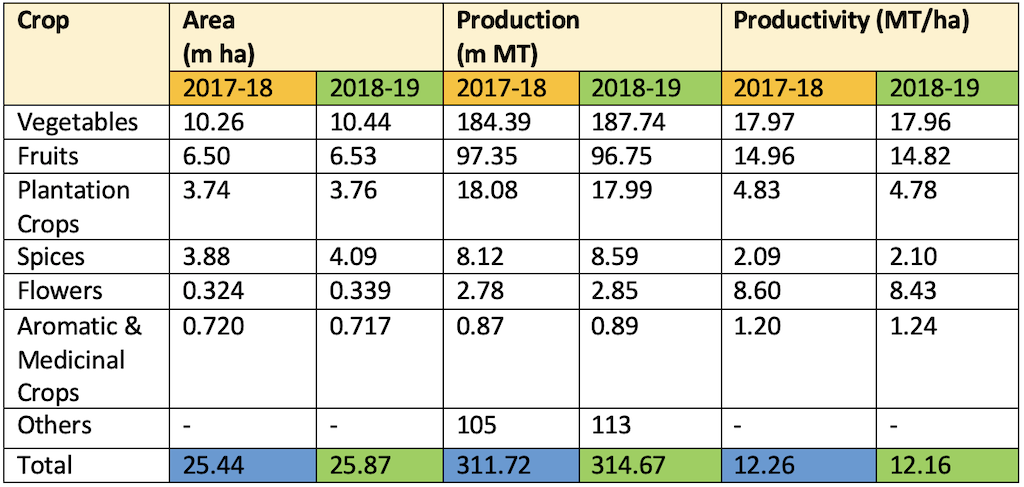
- During 2017-18 the area under vegetables was
10.26 Million Hectareswith a production of184.40 Million Tonnesin India. - For this period the total vegetable production was highest in case of
Uttar Pradeshfollowed by West Bengal. - India witnessed the shift in area from food grain towards horticulture crops over last five years (from 2012-13 to 2017-18). The production of Horticulture crops have outpaced the production of food grain since 2012-13.
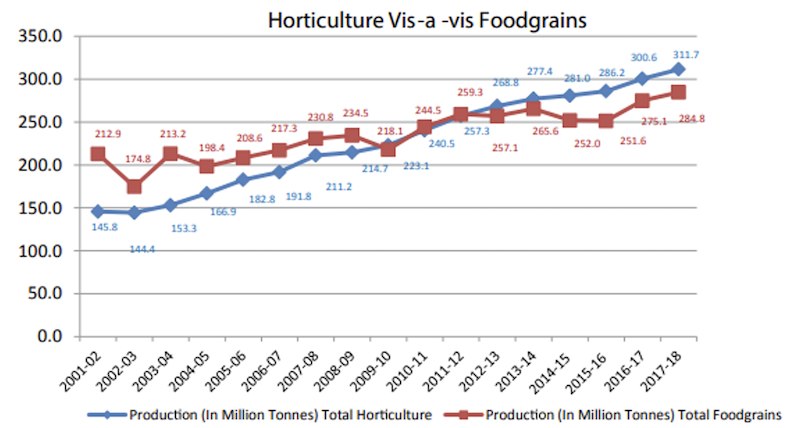
3rd Advance Estimate NHB 2018-19
- There is a marginal increase in the area under horticulture crops. The area in 2018-19 is estimated to be
25.49 million hectares (mh)as compared to 25.43 mh in 2017-18. - There is a marginal increase in the production of horticultural crops from 311.7 to 313.85 milllion tonnes.
- Vegetables occupying an area of 10.10 million ha with total production of 187.37 milllion tonnes with average productivity of 18.56 tonnes/ha.
Fruits (2017-18 NHB)
- India ranked
secondin fruit production (China >India> Brazil). - Total fruit production:
97.35 MT - Area under fruit production: 6.53 M ha
- Productivity of fruit crops: 14.96 tonnes/ha.
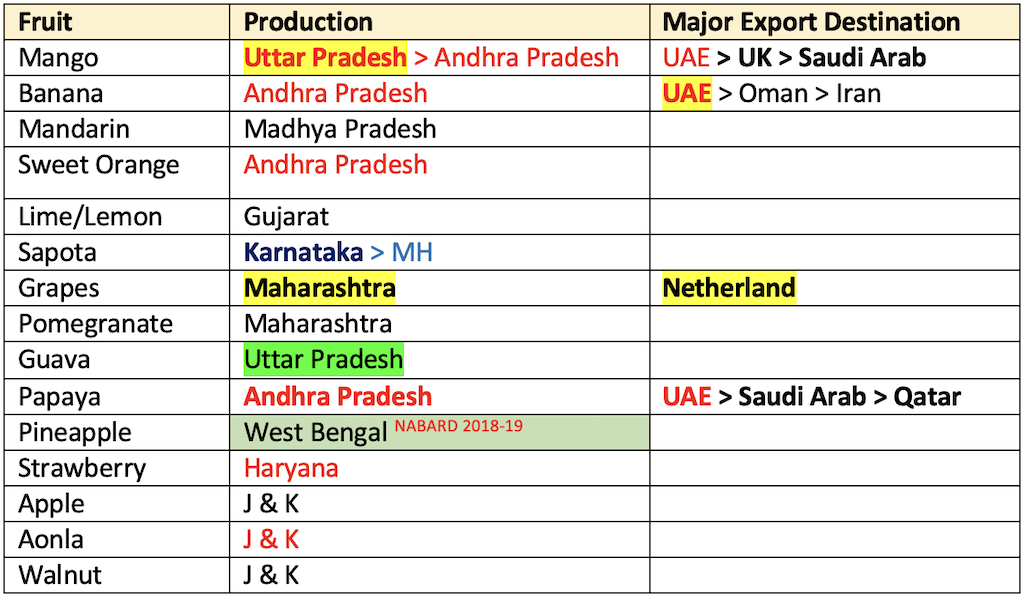
- India is first in the production of fruits like
Mango,Banana,Sapota,PomegranateandAonla. Grapesoccupy premier position in exports with 188.2 thousand tonnes.- Other fruits which have attained position in exports are banana and mango.
- India import fresh fruits & vegetables from:
US> Afghanistan > Iran - India import processed fruits & vegetables from: Afghanistan > China > US
- Largest fruit producing state:
A.P.> M.H. > U.P.
- Fruits leading in area:
Mango>Citrus> Banana > Apple
- Leading in production:
Banana>Mango> Citrus > Apple
Vegetables (2017-18 NHB)
- India ranked
secondin the vegetable production after China. - Total vegetable production:
184.40 Million Tones. - Area under vegetable:
10.27 Million ha. - Productivity of Vegetables:
17.97 tonnes/ha. - India is first in the production of pea and okra and second in production of brinjal, cabbage, cauliflower and onion and third in potato and tomato in the world.
- Total vegetable production:
Uttar Pradesh> West Bengal > M.P.
- Vegetables leading in area:
Potato>Onion>Tomato>Brinjal
- Leading in production:
Potato>Onion>Tomato>Brinjal
Flowers
- India has also made remarkable advancements in production of flowers, particularly cut flowers, which have a high potential for exports.
- Floriculture during 2018-19 (1st Advance Estimate) covered an area of 0.34 million ha with production of
2.86 million MTof flowers. - The highest production of Flowers was recorded in
Tamil Nadu(482.52 Thousand Tonnes) followed by Andhra Pradesh (428.95 Thousand Tonnes). - Area of flower:
J&K> KL > TN
Marigold> Rose > Chrysanthemum
- India import flowers from:
Netherland> Thilland > China - Export of flowers from India:
US> Netherland > UK
Aromatic & Medicinal Plants
- Production:
RJ> TN > MP - Area:
RJ> UP > MP
Spices
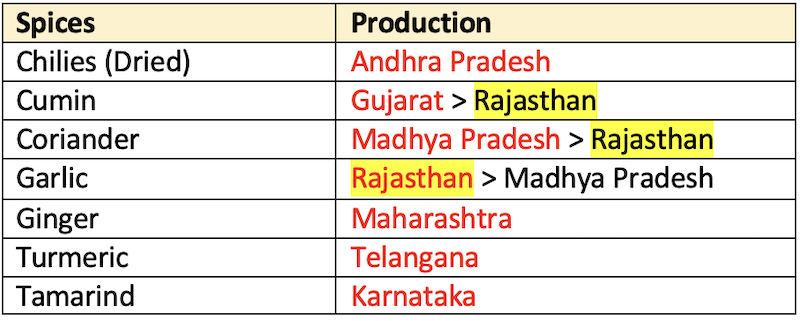
- India is the largest producer, consumer and exporter of spices and spice products, the total production of spices during 2018-19 (1st Advance Estimate) was
8.59 m MTfrom an area of4.06 m ha. - Area:
Cumin> Chillies > Coriander
- Production:
Chillies> Garlic > Turmeric
- Largest
total spicesproducing state:M.P.(15%) > Raj (14%) > A.P. (13%) - Largest
Seed Spicesproducing state: Rajasthan.
Plantation Crops
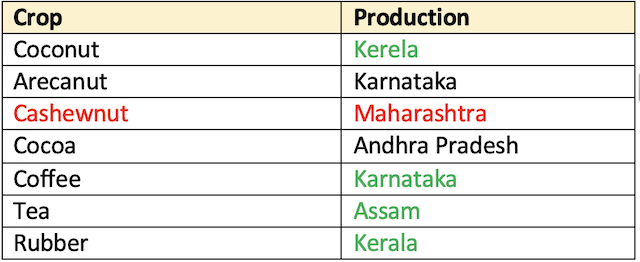
- Area:
Coconut> Cashewnut > Arecanut - Production: Coconut > Arecanut > Cashewnut
- State (Production):
Kerala> KR > TN
- India is the seventh largest producer of coffee, after Brazil, Vietnam, Columbia, Indonesia, Ethiopia and Honduras.
- India accounts for around 2 per cent of the area and 3.7 per cent of the global coffee production.
- The total production in India stood at 3,12,000 MT in 2016-17, of which Robusta variety accounted for 217000 MT (70%) and Arabica accounted for 95000 MT (30%).
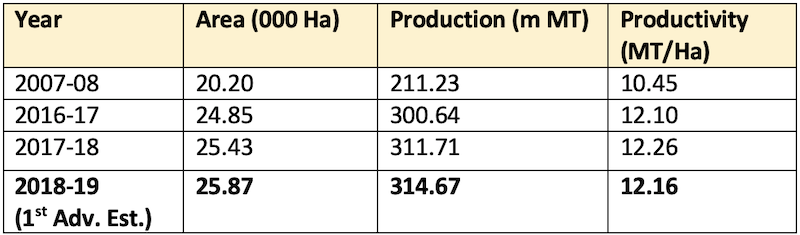
During the period 2007-08 to 2018-19 (1st Advance Estimate)
- Horticulture crops cover an area of
25.87 million ha(m. Ha) at present by registering increase of about 28% as compared to 20.20 m. ha in 2007-08. - However, with a production of about
314.67 million MT) horticulture production has witnessed an increase of about 49% during the period 2007-08 to 2018-19 (1st Advance Estimate). - Interventions in horticulture in the country have led to increase per capita availability of fruits from 158 gm/person/day in 2007-08 to
207.9 gm/person/dayin 2017-18. - Similarly, per capita availability of vegetables has increased from 309 gm/person/day in 2007-08 to
393.76 gm/person/dayin 2017-18.
Interventions in Horticultural Sector by GoI
National Horticultural Mission (NHM)
- The Ministry of Agriculture has been implementing the centrally sponsored NHM for the holistic development of the horticulture sector through an area based regionally differentiated strategy in
2005-06. - 18 states and the 4 UTs are covered under the Mission except the 7 north-eastern states & 3 Himalayan states (J&K, Himachal & UK).
- The latter are covered under the Horticulture Mission for the North East and Himalayan States (HMNEH).
- Now the scheme has been subsumed as a part of Mission for Integration Development of Horticulture (MIDH) during
2014-15. - Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare.
- Sub Schemes of MIDH:
- NHM
- HMNEH
- National Horticultural Board (NHB),
Gurugram - Coconut Development Board (CDB),
Kochi - Central Institute for Horticulture (CIH): Established at Medizipehima,
Nagalandin 2006-07 for providing technical back stopping through capacity building and training of farmers and Field functionaries in the North Eastern Region. - National Bamboo Mission (NBM)
- A Centrally Sponsored scheme.
- Government of India (GOI) contributes 85% of total outlay for developmental programs in all the states except the states in North East and Himalayas, 15% share is contributed by State Governments.
- In the case of North Eastern States and Himalayan States, GOI contribution is 100%.
- Similarly, for development of bamboo and programmes of National Horticulture Board (NHB), Coconut Development Board (CDB), Central Institute for Horticulture (CIH), Nagaland and the National Level Agencies (NLA), GOI contribution will be 100%.
Coconut Development Board (CDB)
- Coconut Development Board is statutory body established by GoI by an Act of Parliament (Coconut Development Board Act 1979) and came in to existence in January
1981. - The coconut palm provide food security and livelihood opportunities to more than 12 million people in India.
- As per all India estimate for the year 2017-18, the area and production of coconut in the country is 2.099 million hectares and 24.38 billion nuts respectively.
- The productivity of coconut at national level for 2017-18 is 11,616 nuts per hectare.
National Bamboo Mission (NBM)
- The Ministry of Agriculture has implemented the centrally sponsored NBM in 27 states in the country in
2006-07. - The mission aims to promote holistic growth of the bamboo sector by adopting an area-based, regionally differentiated strategy and to increase the area under bamboo cultivation and marketing. Under the Mission, steps have been taken to increase the availability of quality planting material by supporting the setting up of new nurseries and strengthening of existing ones. To address forward integration, the Mission is taking steps to strengthen marketing of bamboo products, especially those of handicraft items.
- The Government’s goal in the bamboo sector is being achieved with the concerted efforts of all stakeholders of the Bamboo Mission. Keeping in consideration the importance of bamboo, the Indian Forest Act 1927 was amended in the year
2017to remove bamboo for the category of trees, as a result now anyone can undertake cultivation and business in bamboo and its products. - The Restructured National Bamboo Mission was launched in 2018-19 for holistic development of the complete value chain of the sector. The Mission is being implemented in a hub (industry) and spoke model, with the main goal of connecting farmers to markets so as to enable farmer producers to get a ready market for the bamboo grown and to increase supply of appropriate raw material to domestic industry.
- The Mission was launched as a natural corollary of the historic amendment of the Indian Forest Act in 2017, removing bamboo from the definition of trees, hence bamboo grown outside forests no longer need felling and transit permissions.
- New Logo released for NBM:

Current Status (Final Figures)
- India is
secondlargest producer of horticultural crops. - The scenario of horticulture crops in India has become very encouraging. The percentage share of horticulture GDP to Agriculture has become
32%. (NHB) - Cold Storage:
UP(2368) > GJ (890) > PB (672) in 2017-18.

- In 2017-18, the total horticulture production was highest in case of
Uttar Pradesh(392.48 Lakh Tonnes) followed by West Bengal (324.2 Lakh Tonnes). - The total production of fruits is highest in case of
Andhra Pradesh(152.15 Lakh Tonnes) followed by Maharashtra (117.28 Lakh Tonnes). - Apart from nutritional benefits, the production of vegetables improves the economy of a country as these are very good source of income and employment. The contribution of vegetables remains highest (59 – …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel