🍈 Guava & Aonla
Important points, varities, pests
Guava
- Botanical Name:
Psidium guajava - Family: Myrtaceae
- Origin: Peru
- Also known as apple of poor or poor man’s apple.
- Guava improvement work was started in 1907 at Pune.
Guava-Bahar season
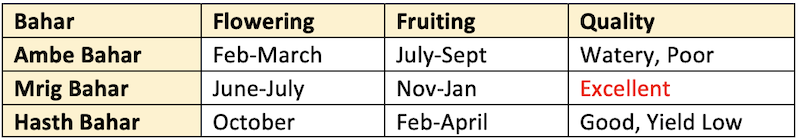
- Fruit bearing takes place 3 times in South India.
- Two type of fruits, completely seedless and partly seeded are borne on the plant of seedless variety.
- Guava harvested throughout year except May and June.
- Chinese guava — P. fridrichsthalianum — dwarfing rootstock and resistant to guava wilt and nematodes.
- High density planting reduces TSS, sugars and ascorbic acid but increases titrable acidity.
L-49is more susceptible to Bronzing than Allahabad safeda.- Fruit quality of winter crop is best, it escapes the attack of fruit flies.
- Practice of taking winter crop instead of rainy season crop is known as
crop regulation(to escapes the attack of fruit flies). - Rainy season crop can be removed by spraying of urea (10%) on Allahabad safeda and 20% on Lucknow-49 at the time of peak flowering period.
Uttar Pradeshproduce-best quality Guava. Allahabad region of UP is known for best quality guava production.- Vitamin-C content highest in fruit peel at mature stage.
- Most useful in human diet for avoiding scury disease.
- Guava wilt is most common in Alkali soil.
- Guava can tolerate salinity but is susceptible to soil acidity.
- Dwarfing rootstock: Anueploid-82.
Stoolingis the most common & cheapest method of guava propagation. Air layering is also done.- Bending in Guava — practiced in Maharashtra.
- Pruning: Above 90 cm, lateral shoots are not allowed to grow.
- Rich source of pectin.
- Meadow orcharding technique was developed in guava for horizontal utilization of space [2.0 m (row to row) x 1.0 m (plant to plant)].

Varieties
Behat coconut:Seedless GuavaLucknow-49 (Sardar):Chance seedling selection from Allahabad Safeda in 1927 in Pune by Dr. Cheema.Allahabad Safeda:famous variety of AllahabadLalit:24% higher yield than Allahabad Safeda. Pink flesh. Suitable for Jelly making.- Chittidar: Fruits are characterized by numerous red dots on skin.
- Harijha: Most popular in Bihar.
- Hafsi: Red fleshed guava.
- Apple colour
- Arka mridula: Seedling selection from Allahabad safeda, soft seeded variety.
- Allahabad round: Parthenocarpic variety
- Allahabad Surkha: Uniform pink fruit with deep pink flesh.
- Saharanpur seedless
- Nagpur seedless

- Arka Amulya: Arka Safeda x Seedless
- Hissar Surekha
- Shweta: High TSS (140° Brix)
Hybrid
- Kohir Safed: Kohir X AS (Allahabad Safed)
- Safed Jam: AS X Kohli
- Hybrid-45: AS x L-49 (Sardar)
Disease
- Guava wilt
- Fusariunt oxysporium p.v. Psidii
- Wilting appearance of plants and leaves of young plants is dries up.
- Wilt is serious problem in guava (common in Alkali soil)
- Management
- Soil drench with Carbendazim/Bavistin @ 2g/liter water.
- Grow resistant varieties i.e. Allahabad Safeda.
Insect pest
-
Striped mealy bug:
Ferrisa virgata, serious pest in South India
-
Guava tea mosquito bug:
Helopeltis antonh
Physiological disorder
- Bronzing: Due to
Zndeficiency
Aonla
Emblica officinalis(Euphorbiaceae)- It is also known as Indian gooseberry is an indigenous fruit.
- Propagation by patch budding in North India.
- Aonla fruits is contains vitamin C 600 mg/100g.
- Large sized, sound fruits are mostly utilized for preservation and candy
- Bearing life of anona is 65 to 70 years.
Varieties

Disease
-
Ring rust: Ravenelia emblica, it is serious disease in aonla.

-
Fruit necrosis: B-deficiency. Francis variety highly suffered
Insect
- Bark eating caterpillar: Indarbella quadrinotata
Guava
- Botanical Name:
Psidium guajava - Family: Myrtaceae
- Origin: Peru
- Also known as apple of poor or poor man’s apple.
- Guava improvement work was started in 1907 at Pune.
Guava-Bahar season

- Fruit bearing takes place 3 times in South India.
- Two type of fruits, completely seedless and partly seeded are borne on the plant of seedless variety.
- Guava harvested throughout year except May and June.
- Chinese guava — P. fridrichsthalianum — dwarfing rootstock and resistant to guava wilt and nematodes.
- High density planting reduces TSS, sugars and ascorbic acid but increases titrable acidity.
L-49is more susceptible to Bronzing than Allahabad safeda.- Fruit quality of winter crop is best, it escapes the attack of fruit flies.
- Practice of taking winter crop instead of rainy season crop is known …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel