🥭 Mango
Important points, botany, varities, pests
- Botanical Name: Mangifera indica
- Family: Anacardiaceae
- Origin: Indo-Burma region
- India first in mango production in the world. About 39% of world mango are produced in India.
- U.P. first in mango production in India.
- Highest productivity in the world: Venezuela
National fruit of India/ King of Fruits.- Pollinator: house fly
- Mango can withstand deficiency of P but not K.
- VHT (Vapour heat treatment) is recommended for disinfection of mango against fruit flies and stone weevil.
- Two crop of mango is taken in Kanyakumari district of TN.
- Mango hybridization work was first started by Burns and Prayag in 1911 at Pune.
- Caging technique of breeding was used in mango by Dr. R.N. Singh.
- Black tip was first observed in 1909 by Woodhouse.
- Spongy tissue was first observed by Cheema and Dhani in 1934.
- Good mango varieties have a TSS of 20 %.
- Xavier - variety have highest TSS -
24.8 Brix. - Maturity indices:
Alphonso-SG-1.01 to 1.02 (SG)- Specific gravityDashehari-SG-1.0 - No. of perfect (bisexual) flower: Highest— 68.9% in Langra variety, Lowest— 0.74% Rumani variety.
Flower


- Mango has male and hermaphrodite flowers.
- In mango, only 0.1% flower (perfect) develops fruits to maturity.
- Spray 2-4-D 10 PPM, to overcome this problem.
- Temperature between
24-27 °Cis ideal for mango cultivation. - Mangoes are highly susceptible to low temperature injury that’s why they should be stored
above 5 °Ctemperature during storage. - Storage temperature:
- Mature fruit 6 - 7 °C
- Ripened fruit 20 °C
- Longevity of mango seeds: 30 days (4 weeks)
Field preparation
- Dig pits of 1 m x 1 m x 1 m fill in with topsoil mixed with 10 kg of FYM per pit.
Spacing
- Adopt any one of the following spacing depending on requirements.
- Under conventional system of planting: 7 - 10 m either way
- High Density Planting: 5m x 5m (400 plants/ha)
- Double hedge row system: Adopt a spacing of 5m x 5m within double rows and 10m between successive double rows (266 plants/ha)
Planting
- Grafting: Grafts are planted in the center of pit with ball of earth intact followed by watering and staking.
- The graft union must be 15 cm above the ground level.

Growth regulators
- NAA @ 20 ppm is sprayed at flowering to increase the fruit retention.
- Spraying of 2% KNO3 at mustard size will increase the fruit set and retention of fruits.
- Application of
Paclobutrazol@ 10 g i.e. for **non-bearing trees **during first fortnight of September will induce flowering and fruit set yield during off years.
Varieties
Types of Mango varieties
- North Indian cultivar: These are alternate bearer, monoembryonic, self-incompatible.
- South Indian varieties: These are regular bearing, polyembryonic.
- Regular bearing varieties: Neelum, Totapuri, Pairi, Gulabkhas, Himsagar.
- Alternate bearer: Langra and Deshehari
- Off season bearing: Niranjan and Madhulica
- Poly embryonic varieties: Goa, Mulgoa, Olour, Bellary, Chandrakaran
- Exotic coloured cultivars: Tommy Atkins, Zilette, Haden, Sensation, Julie
Mulgoais mother of all coloured cultivars of mango and useful for making preserve.- Polyembryonic rootstocks of mango:
- Goa
- Mulgoa
- Olour
- Bellary
- Chandrakaran
- Villiacolumban
- Kurukkan
- Solan
- Bappakai
- Nileshwar dwarf
- Rumani is used for dwarfing effect in Dashehari.
- Olour is used for dwarfing effect in Langra & Himsagar
- Villicolumban is used for dwarfing effect in Alphonso.
- Salt resistant rootstock of mango: Kurukkan, Moovandan, Nekkare
- Malbhog variety of mango is most susceptible to water logged conditions.
- Dasheheri variety have high fruit retention.
- Langra variety have highest number of perfect flowers.
- Mango variety Mulgoa is mono-embryonic in India and polyembryonic in Florida.
- Dashehari, Langra, Chausa and Bombay green are self-incompatible mango cultivars.
- Besides Alphonso, Kesar, Gulabkhas, Lakhan bhog, Safdar pasand are exported.
- Rosica: Mutant variety of mango.
- Madhulica: Most precocious cultivar of mango.
- Mankurad
- Banglora
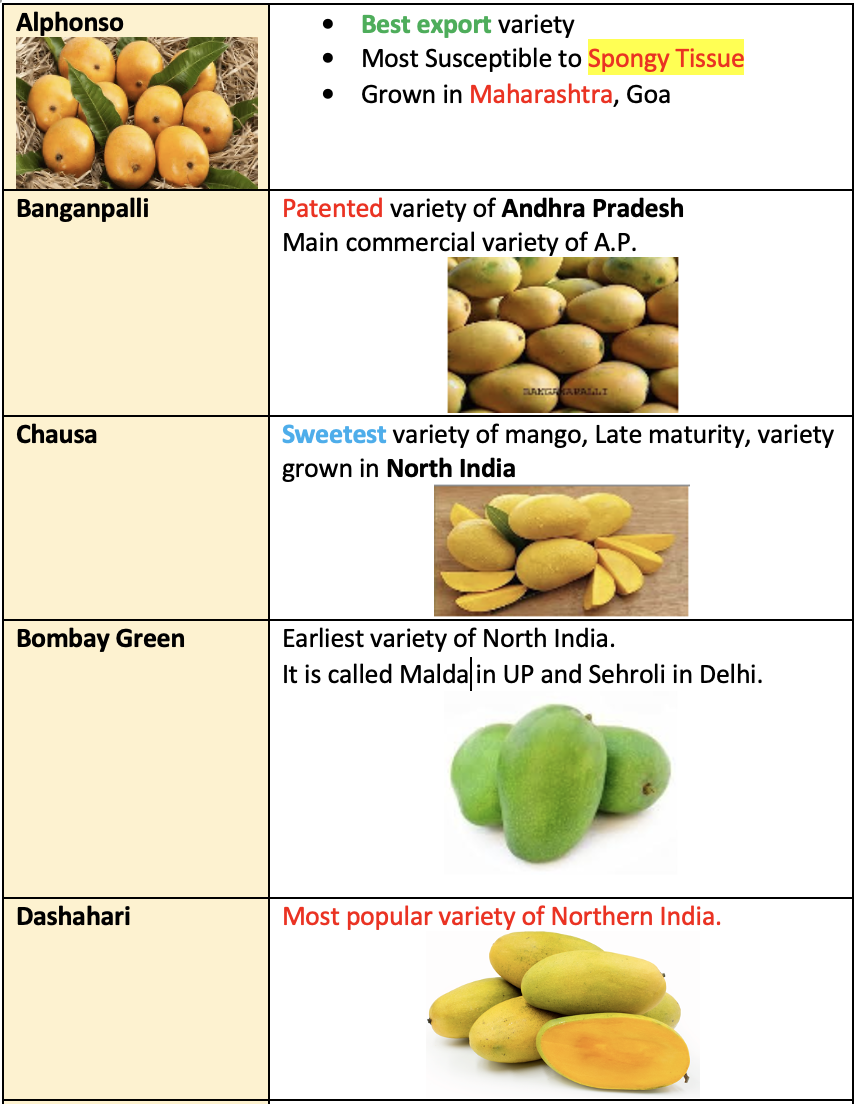
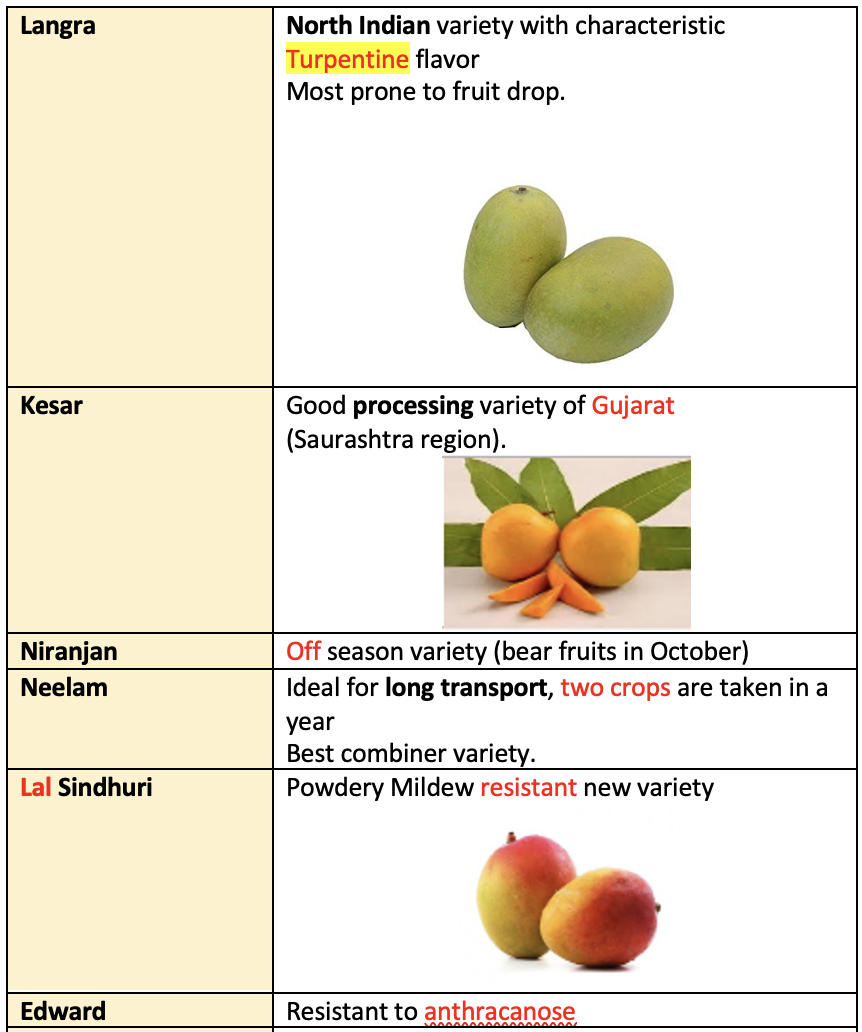

GI certified Mango variety

Hybrid Varieties

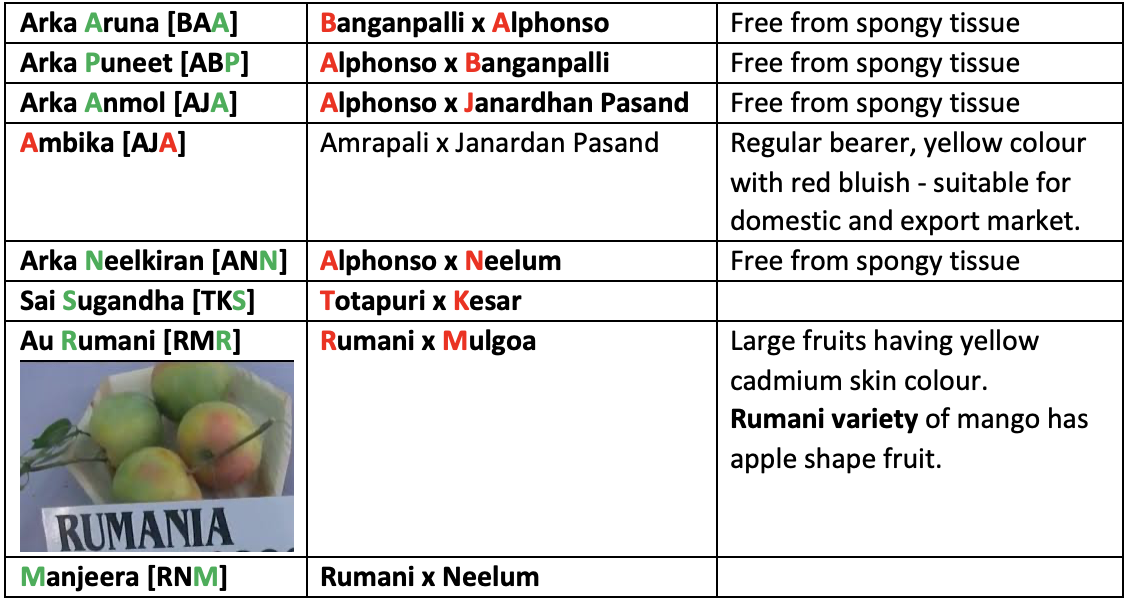
- ICAR-IIHR developed a new double cross hybrid between Amrapali (Dashehari x Neelam) x Arka Anmol (Alphonso x Janardhan Pasand). UPPSC 2021
New Varieties Released by IARI
- Pusa Surya
- Pusa Arumina: Cross between Amrapalli x Sensation (USA variety)
- Akshay: Selection from Dashehari
- Sai Sugantha: Cross between Totapuri x Kesar: Regular bear, free from malformation suitable for pulp making.
Harvesting
- Flowering occur in January and harvesting is done in May to June.
Disorders
Alternate bearing
- On year: Bears flowering.
- Off year: Bears no flowering.
- Alternate bearing has been one of the major problems.
- Most of the South Indian varieties are regular-bearer
- North Indian ones alternate-bearer.
- It is problem especially in Dashehari, Langra and Chausa.
- Management:

- Cultar (Paclobutrazol) (5-10 gm/tree) is a promising chemical for flower induction in mango.
- Planting regular bearing varieties: Amrapali, Neelam, Ratna etc.
Black tip (Due to deficiency of boron)
- Near brick kilns distal end of affected fruits get turned black and become hardened.
- Smoke of brick - kilns containing gases like CO, CO2, SO2 & Acetylenes are responsible for this.
- Management:
- Orchard planting away from brick kilns at least 1 km distance.
- Three spray of borax (0.6%) (before flowering, during flowering and at fruit set)
- Borax contains: 11% boron.

Clustering (Jhumka)
- This malady is characterized by a cluster of fruitlets at the tip of the panicle giving an appearance of bunch tip called jhumka.
- Such fruits cease to grow beyond pea or marble stage and drop down after a month of fruit set.

Spongy tissue/ Internal Break down
- Major problem in Alphonso mango.
- Fruits from outside look normal. But inside a patch of flesh becomes spongy, yellowish and sour. BOM AFO
- This disorder has brought down the export of this variety.
- Inactivation of ripening enzyme due to high temperature, convective heat and post-harvest exposure to sunlight are the causes.
- Resistant varieties: Neelam and Deshehari are almost free from it.
- Other new resistant varieties: Arka aruna, Ratna, Arka puneet, Arka anmol etc. are free from spongy tissue.

Leaf scorching
- Due to Potassium deficiency.
- Spray Potassium Sulphate 5%.
Internal necrosis
Borondeficiency.- Management:
- Application of boron /borax @ 0.6 %
Little leaf of Mango
- Due to deficiency of
Zn.
Insects
- Mano mealy bug:
Drasicha mangiferae: Major pest of Mango - Mango hopper
- Mango Fruit Fly
- Stem borerStone weevil
Disease
- Powdery mildew (Major)
- Mango Malformation: Mango malformation was first observed in 1891 in Bihar.
- Anthracnose
- Sooty Mould
- Botanical Name: Mangifera indica
- Family: Anacardiaceae
- Origin: Indo-Burma region
- India first in mango production in the world. About 39% of world mango are produced in India.
- U.P. first in mango production in India.
- Highest productivity in the world: Venezuela
National fruit of India/ King of Fruits.- Pollinator: house fly
- Mango can withstand deficiency of P but not K.
- VHT (Vapour heat treatment) is recommended for disinfection of mango against fruit flies and stone weevil.
- Two crop of mango is taken in Kanyakumari district of TN.
- Mango hybridization work was first started by Burns and Prayag in 1911 at Pune.
- Caging technique of breeding was used in mango by Dr. R.N. Singh.
- Black tip was first observed in 1909 by Woodhouse.
- Spongy tissue was first observed by Cheema and Dhani in 1934.
- Good …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel