🍅 Pomegranate
Important points, varities, pests
- Botanical Name:
Punica grananun - Family: Punicaceae
- Origin: Iran
- It is highly drought tolerant among fruit crops.
- Pigment responsible for the red colour in pomegranate fruits is
Anthocyanin. - India has first position in the world with respect to pomegranate area and production.
- In India Maharashtra is the leading state in area and production followed by KR, AP, GJ, TN and RAJ.
- Juice of pomegranate is useful for patient suffering from leprosy.
- July-August is ideal time of planting in tropics.
- Wild type Anar is known is Daru.
- Presently
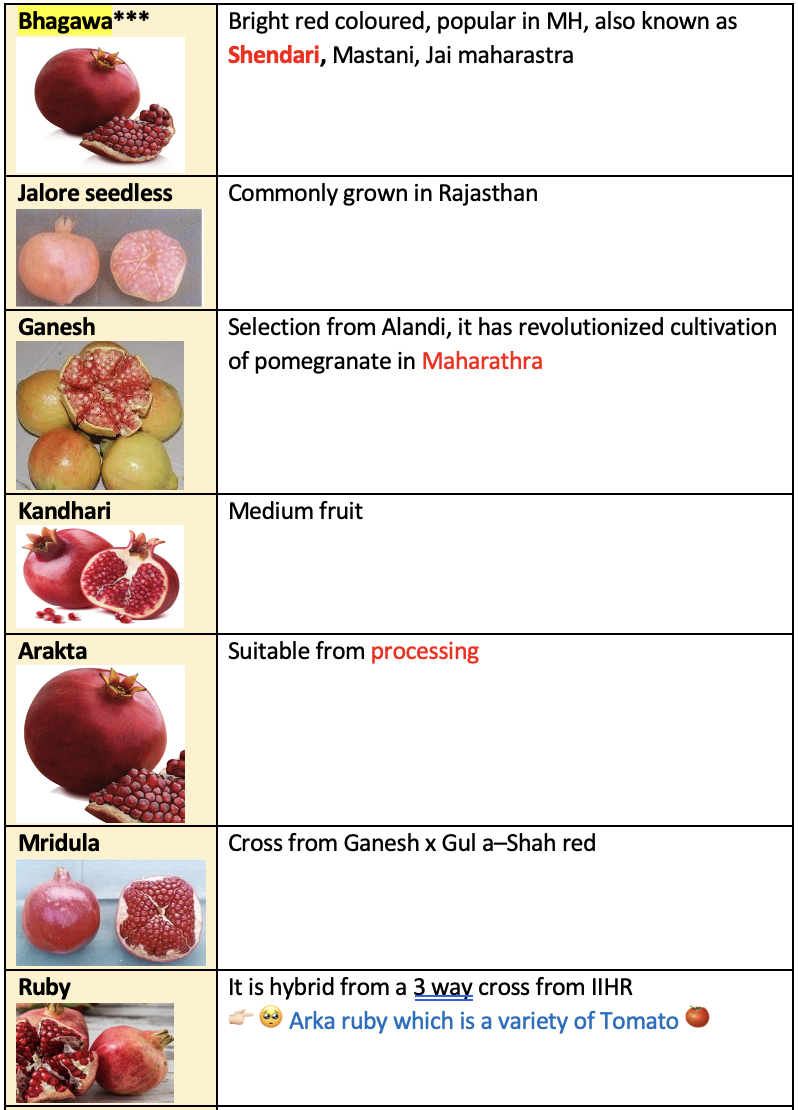
Bhagawais the leading variety of pomegranate cultivation in India especially in Maharashtra. - Propagated by stem cutting (Hardwood Cutting) and air layering (Gootee).
- Wood younger than 6 months and older than 18 months is unsuitable for cutting.
- Multi stem training system is followed in India.
- Anti-transpirants such as 10% kaolin, 10-5 m phenyl mercuric acetate, 1.5% power oil, 1% liquid paraffin is beneficial for increasing its productivity.
- Summer crop maximum demand.
- Root treatment with 3000 ppm IBA gives maximum survival.
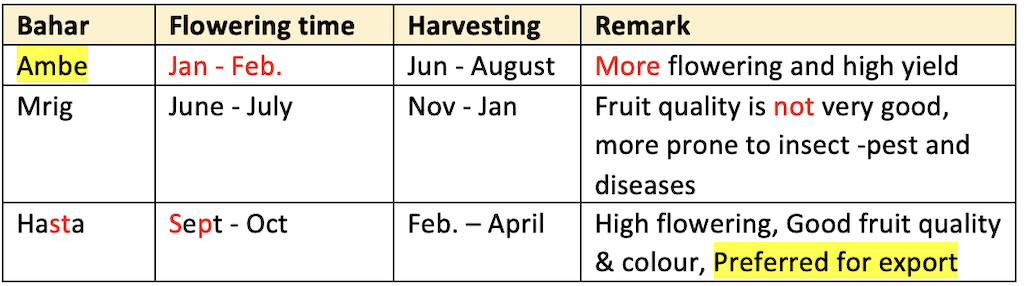
- Bahar treatment is followed in pomegranate.
- Ambe bahar is most commonly preferred by the growers because of high yield as compared to other flowering season.
- More incidence of fruit cracking (Internal break down) takes place in mrig bahar season.
Varieties

- Solapur Lal
- Muskati red
- Paper shelled
- Alandi
- Karadi
- Madhugiri
- Bassein seedless
- Chawla
- Country large red
- Spanish Ruby
- Muskat
- Nabha
- G-137: Clonal selection from Ganesh.
- P-26: Seedling selection from muscat.
- Jyoli: Bassein seedless x Dholka
Hybrid
- Ruby: Ganesh x Kabul x Yercaud
- Soft seeded var: 1. Jyothi 2. Ganesh 3. Bassein seedless 4. Paper shell
- Hard seeded var: 1. Khandhari 2. Alandi
Insects
- Anar butterfly: Virachola isocrates

- Serious pest of pomegranate
- Pencil size bored holes can be seen on fruits from which larval excreta comes out continuously.
- It is managed by Covering of fruits with butter paper.
- Spray Carbaryl 50 WP @ 2-4 g/liter or Methomyl 40 SP @ 1.0 ml/l or Monocrotophos 36 SL @ 1 ml/liter spray on plants.
- Fruit fly:
- Bactrocera zonata
- Minor pest of pomegranate

- Fruit sucking moth:
- Othreis spp.
Disease
- Bacterial blight:
- Caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae

- Also known as nodal blight or black spot
- In Maharashtra commonly known as oily spot or Telya.
Physiological disorder
- Fruit cracking:
- Due to
B deficiency.
- Due to

- More in Rajasthan (dry areas).
- Managed by spray of Borax @ 0.5 %.
Internal breakdown
- Disintegration of arils in matured pomegranate.
- Arils become brown and blackening.
- The incidence is more in ambe bahar (Jan - June)
- Botanical Name:
Punica grananun - Family: Punicaceae
- Origin: Iran
- It is highly drought tolerant among fruit crops.
- Pigment responsible for the red colour in pomegranate fruits is
Anthocyanin. - India has first position in the world with respect to pomegranate area and production.
- In India Maharashtra is the leading state in area and production followed by KR, AP, GJ, TN and RAJ.
- Juice of pomegranate is useful for patient suffering from leprosy.
- July-August is ideal time of planting in tropics.
- Wild type Anar is known is Daru.
- Presently
Bhagawais the leading variety of pomegranate cultivation in India especially in Maharashtra. - Propagated by stem cutting (Hardwood Cutting) and air layering (Gootee).
- Wood younger than 6 months and older than 18 months is unsuitable for cutting.
- Multi stem …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel