🍶 Preservation
Principles of Preservation, Maturity Indices of Fruits
- Highest food processing industries is in
Andhra Pradesh.
Fruit preservation
- The art and science of keeping fruits for longer time without detonation in quality.
Principle of preservation
Canning
- It is method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like mason jars and steel and tin cans).
- Packed in vacuum.
- Fruits can be processed at a temperature of
100 °C. - Vegetable can be processed at temperature of
115-121 °C. - Lidding or Clinching
- Cans after being filled, are covered loosely with lid and passed through the exhaust box.
- Lidding is now replaced by clinching in which the lid is partially seamed to the can by a single first roller action of double seamer.

Pasteurization
- Heating of fruits and vegetable juice at
85-90 °Cfor 30 minutes. - It kills only harmful microbes.
Sterilization
- Heating of fruits and vegetables
above 100 °C - It kills both beneficial and harmful bacteria.
Freezing
- Cooler storage:
15 °C - Refrigeration or chilling:
0 - 5 °C
Cry preservation
- Preserve in
liquid nitrogenat -196 °C.
Lyophilization or Cryodesiccation
Freezedrying, also known as lyophilization or cryodesiccation, is a low temperature dehydration process that involves freezing the product, lowering pressure, then removing the ice by sublimation.- This contrasts with dehydration by most conventional methods that evaporate water using heat.
Drying
- Removal of moisture by applying heat is called drying.
- E.g. Raisins (Kismis).
Preservation through osmosis
- High concentration of sugar.
- E.g. Jam (68 % sugar), Agari ka petha.
Salt preservation:
- Salt conc. 10-25 % is sufficient (in pickles: 15%).
Preservation by chemicals
- KMS (Potassium Meta bi Sulphite): @ 500 ppm/0.05%.
- Sulphur di oxide is responsible for preservation.
- It used against
colour lessfruit Juices/pulp.
- Sodium benzoate: @ 700 ppm/0.07%.
- Benzoic acid is responsible for preservation.
- Used in
colored fruit(only in non-acid fruits).
Fermentation
- Grape wine (alcohol 7-20%) is oldest example of fermented beverage.
Asepsis
- Prevent entry of microbes.
Oxidation
- Oxidation can be checked by antioxidants (Ascorbic acid /vit. C)
Enzymes
- Checking of enzymatic spoiling:
Blanchingin cauliflower Clostridium pasteurianumis a beneficial bacteria for fruit preservation industry. UPPSC 2021
Waxing
- Wax coating treatment enhance the shelf life of fruit by inhibiting respiration.
Maturity Indices of Fruits
👉🏻 Symptoms which indicate that fruits are ready to harvest:
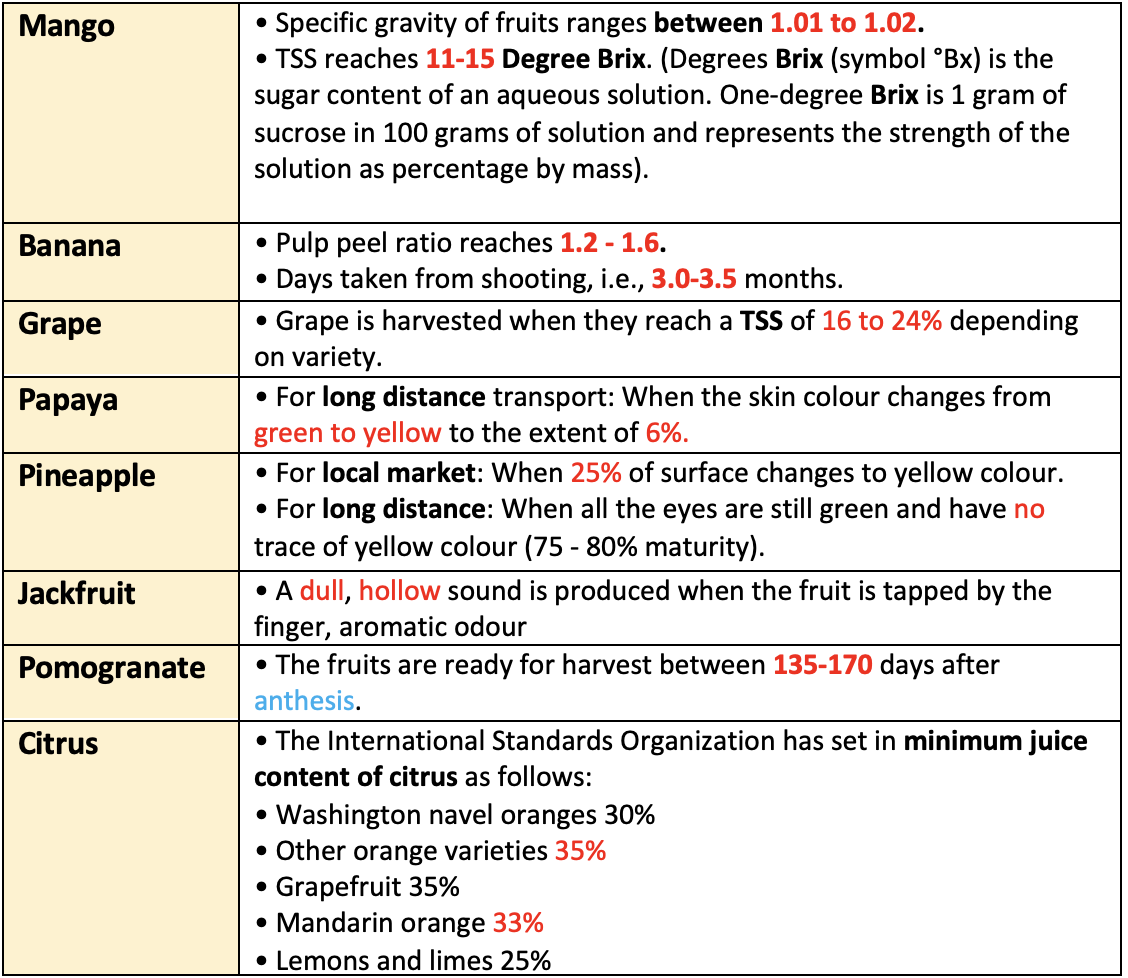
Post Harvest Handling
Degreening of fruit is a post-harvest process by which the green color is removed from the peel by treating the fruit with ethylene gas to degrade chlorophyll and reveal yellow and orange colors for commercial and marketing purposes.
Explore More 🔭
- Highest food processing industries is in
Andhra Pradesh.
Fruit preservation
- The art and science of keeping fruits for longer time without detonation in quality.
Principle of preservation
Canning
- It is method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like mason jars and steel and tin cans).
- Packed in vacuum.
- Fruits can be processed at a temperature of
100 °C. - Vegetable can be processed at temperature of
115-121 °C. - Lidding or Clinching
- Cans after being filled, are covered loosely with lid and passed through the exhaust box.
- Lidding is now replaced by clinching in which the lid is partially seamed to the can by a single first roller action of double seamer.

Pasteurization
- Heating of fruits and vegetable juice at
85-90 °Cfor 30 …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel