🧚🏼♂️ Phosphorous
Forms, Fixation, Function, Deficiency, Toxicity
- Phosphorus is taken up by the plant in the form of H2PO4-, HPO4-2, PO4-3 through diffusion and mass flow action.
- The P availability mainly depends on pH. In acid soils (Al & Fe) the presence of Al, Fe, Mn, P gets fixed as AlPO4, FePO4 and not available to the plants. Some times as CaPO4. These are insoluble in H2O.
- Under hilly areas (or) high rainfall areas, all the cations will be leached leaving Fe, Al and Mn. The P availability will be reduced.
- Ideal pH for available P =>
6.5 - 7.5 - If pH > 8.5 the fixation will be more & < 6.5 the fixation will be more.
Forms of P
- Organic P: Nucleic acid and Phospho lipid
- Rock Phosphate - acid soluble. If the organic matter content is high the availability of P is more since it is soluble in acid. It is highly suited to plantation crops. Rock Phosphates is black in colour. Roots also exudates acids, which will solublises the P.
- Fixation is high so the P2O5 deficiency is 15 – 35%.
Phosphorus Mineralization
- C : N : P = 100 : 10 : 1 and if C: P ratio is more than 100 : 1 => immobilization of ‘P’ occurs.
Soil P its origin and Nature
- Soil P exists in many primary and secondary compounds.
- The
apatitegroup of primary minerals is the original source i.e. 55% of soil P.
Fixation of phosphorus in soil UPPSC 2021
- Phosphorus occurs in most plants in concentrations between 0.1 and 0.4%.
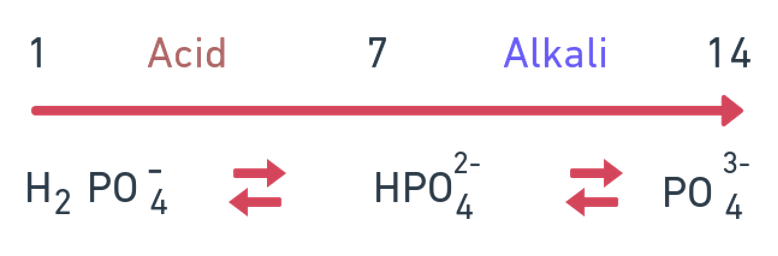
- Plants absorb either H2PO4- or HPO42- Ortho PO43- ions
- Absorption of H2PO4- is greatest at low pH values, whereas uptake of HPO42- is greater at higher values of soil pH, plant uptake of HPO42- is much slower than H2PO4-
Available form of P in acid soil
H2PO4- In less alkali or neutral: HPO42- and when alkalinity is more i.e. high pH: PO43-.
👉🏻 The factors affecting P fixation are:
- Clay minerals
- The PO4 is fixed by clay minerals by reacting with soluble aluminum which originates from the exchange sites or from lattice dissociation to from a highly insoluble AlPO4.
- Iron and Aluminum (fixation in acid soils)
- The formation of Iron and aluminum PO4 in the soil results from the combination of P with these metals in solution and their oxides hydroxides in acid soil.
- 2Al + 3 H2PO4 → Al2 (PO4)3 + 2 H2O + 2H+
- Exchange cations and calcium carbonate (Fixation alkaline soils)
- In calcareous soils, free CaCO3 is a potent source for ‘P’ fixation. P fixation in calcareous soil involved a rapid monolayer sorption of P in dilute concentration. In CaCO3 surfaces and form less soluble compounds of di and tricalcium PO4.
- Ca(H2PO4)2 + 2CaCO3 → Ca3(PO4)2 + 2CO2 + 2 H2O
- Organic matter
- Organic PO4 can be fixed by soil organic matter also influences in Organic PO4 fixation.
- The acids produced during the transformations of Organic matter could decreases the pH and increases fixation by the solubilization of Fe and Al.
Functions

- Due to deficiency of single element phosphorus, plants cannot complete their life cycle hence ‘P’ is called
key to life. - Nitrogen governs the above earth growth whereas ‘P’ governs the root growth i.e. below earth growth.
- It has a greater role in energy storage and transfer.
- It is a constituent of nucleic acid, phytin and phospholipids.
- It is essential for cell division and development. (Meristem Region)
- P compounds act as
energy currencywithin plants. The most common P energy currency is that found in ADP and ATP. Transfer of the energy rich PO4 molecules from ATP to energy requiring substances in the plant is known as “Phosphorylation” - It stimulates early root development and growth and there by helps to establish seedlings quickly.
- It gives rapid and vigorous start to plants strengthens straw and decreases lodging tendency.
- It is essential for
seed formationbecause larger quantities of P is found in seeds and fruits. Phytic acid is the principle storage from of phosphorus in seeds. - Counteracts the excess N. Increases grain to straw ratio.
- Increases Rhizobia activity, increases the formation of root nodules thus helping in more N - fixation.
Deficiency of P
👉🏻 P is mobile in plants and when a deficiency occurs it is translocated from older tissues to the active meristematic regions.
- The marked effect of P deficiency is retarding overall growth. [
Late Maturity] - Leaves will show characteristic bluish green colour.

- It arrests metabolism resulting in reduction of total N of Plants.
- Reduced sugar content. Poor seed and fruit development.
- Premature leaf fall. Restrict root growth.
- Develops necrotic area on the leaf petiole and in the fruit.
Toxicity of phosphorus
- Profuse root growth i.e. lateral and fibrous root lets. [Early maturity and less overall growth]
- It develops normal growth having green leaf colour.
- It may cause in some cases trace elements deficiencies i.e. Zinc and Iron.
Explore More 🔭
🟢 Strengths and weaknesses of acids and bases
References
- Tisdale, S.L., Nelson, W.L., Beaton, J.D. Havlin, J.L.1997. Soil fertility and Fertilizers. Fifth edition, Prentice hall of India Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi
- Singh, S.S.1995. Soil fertility and Nutrient Management. Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana
- Maliwal, G.L. and Somani, L.L. 2011. Soil Technology. Agrotech
- Phosphorus is taken up by the plant in the form of H2PO4-, HPO4-2, PO4-3 through diffusion and mass flow action.
- The P availability mainly depends on pH. In acid soils (Al & Fe) the presence of Al, Fe, Mn, P gets fixed as AlPO4, FePO4 and not available to the plants. Some times as CaPO4. These are insoluble in H2O.
- Under hilly areas (or) high rainfall areas, all the cations will be leached leaving Fe, Al and Mn. The P availability will be reduced.
- Ideal pH for available P =>
6.5 - 7.5 - If pH > 8.5 the fixation will be more & < 6.5 the fixation will be more.
Forms of P
- Organic P: Nucleic acid and Phospho lipid
- Rock Phosphate - acid soluble. If the organic matter content is high the availability of P is more since it is soluble in acid. It is highly suited to plantation …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel