🧱 Soil
Defination, Composition of air and soil
“The science dealing with soil as a natural resource on the surface of the earth, including Pedology (soil genesis, classification and mapping), physical, chemical, biological and fertility properties of soil and these properties in relation to their management for crop production.”
👉🏻 Soil Science has six well defined and developed disciplines:
- Soil Fertility → Nutrient supplying properties of soil
- Soil Chemistry → Chemical constituents, chemical properties and the chemical reactions
- Soil Physics → Involves the study of physical properties
- Soil Microbiology → Deals with microorganisms, its population, classification, its role in transformations
- Soil Conservation → Dealing with protection of soil against physical loss by erosion or against chemical deterioration i.e. excessive loss of nutrients either natural or artificial means.
- Soil Pedology → Dealing with the genesis, survey and classification
Soil occupies the pedosphere, one of Earth’s spheres that the geosciences use to organize the Earth conceptually.
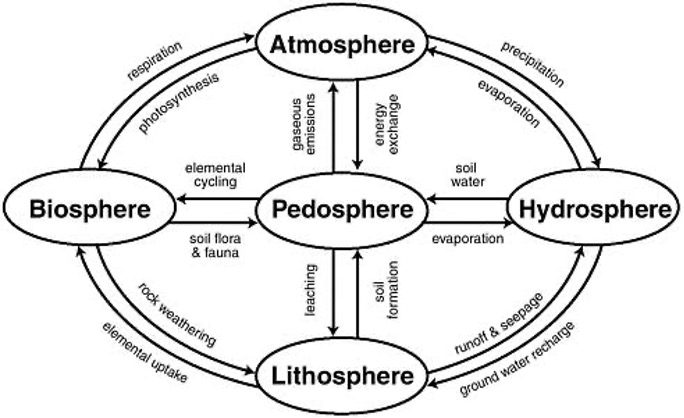
- Solid lithosphere, Liquid hydrosphere and gaseous atmosphere. The atmosphere is of 320 km above the lithosphere / hydrosphere. (70% of Earth’s surface is covered by water (Hydrosphere).
👉🏻 Composition of Atmospheric Air
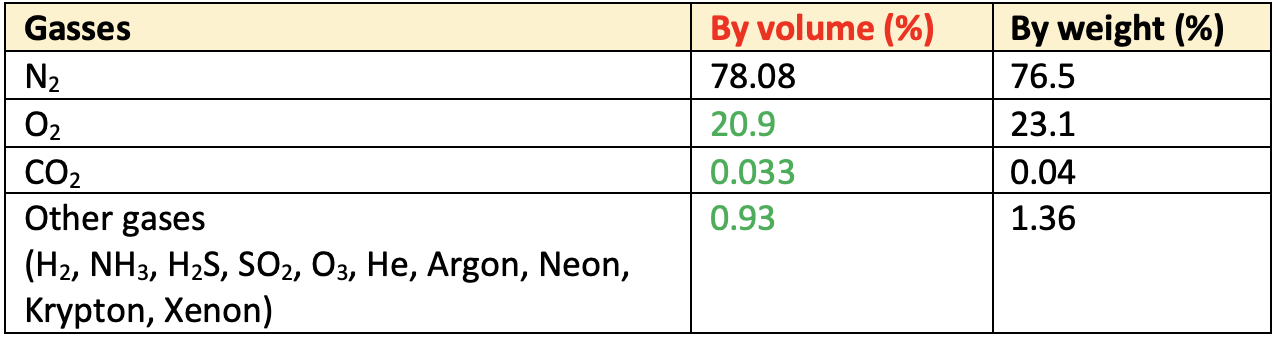
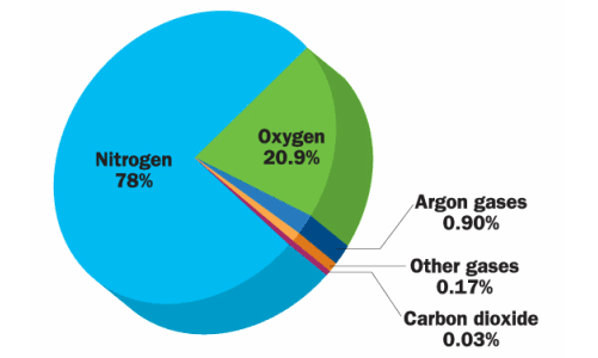
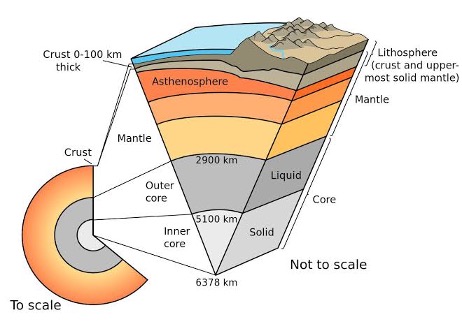
- The Earth’s crust is principally composed of mineral matter. This mineral matter is made up of various elements combined together to form compounds. Some elements exist as such without forming compounds. Almost all the elements known to us at present, except the inert gases, are present in the earth’s crust.
- The elements do not exist in the earth’s crust as such. Each element is in combination with one or more other elements to form definite chemical compounds known as minerals. Many of these minerals in turn combine together to form aggregates, which we know as rocks. Almost all the mineral matter is present in the form of rocks in the earth’s crust.
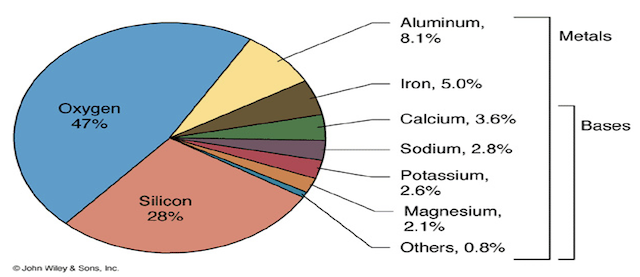
- Generally soil is the porous, powdery and unconsolidated outer layer of the earth’s crust which is formed by weathering of minerals and decomposition of organic substances.
Views on Soil (Science)
👉🏻 The term SOIL was derived from the Latin Word “SOLUM” Means FLOOR
- For a Layman soil is dirt or debris
- For an Agriculturist soil is a habitat for plant growth (to grow crops)
- For a Mining Engineer soil is a debris covering the Rocks
- For a Civil Engineer soil is a material on which road bed or house bed is formed
- For a Home Owner soil is a mellow or loamy or hard material
Soil Science Society of America (1970)
- Soil is the unconsolidated mineral matter on the surface of the earth that has been subjected to and influenced by genetic and environmental factors of parent material, climate (including moisture and temperature effects), macro and microorganisms and topography, all affecting over a period of time and producing a product, that is “SOIL” that differs from the material from which it is derived in many, physical, chemical, biological and morphological properties and characteristics.
- The unconsolidated mineral material on the immediate surface of the earth that serves as a natural medium for the growth of land plants.
- As soil provides nutrients, water, air and anchorage and supports life on Earth, it can be called as
Soul of Infinite Life(SOIL).
Soil as a three dimensional body
- Soil is a three dimensional body having length, breadth and depth.
- They form a continuation over the land surface and differ in properties from place to place.
- Its upper boundary is air or water and lower boundary is the rock lithosphere.
Composition of soil
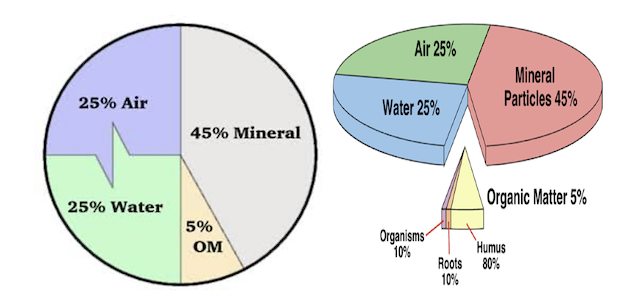
- On Volume Basis (Soil Components)
- Mineral matter: 45%
- Organic matter: 5%
- Soil water: 25%
- Soil air: 25%
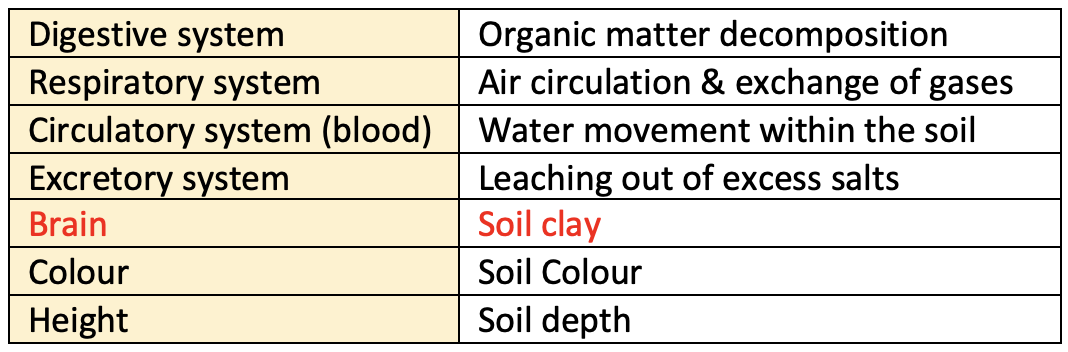
👉🏻 Soil can be compared to various systems of animals
Approaches of Soil
- One treats soil as a natural body, weathered and synthesized product in nature (Pedology) while other treats soil as a medium/habitat for plant growth (Edaphology).
- Pedological Approach: The origin of the soil, its classification and its description are examined in Pedology. (From Greek word pedon, means soil or earth). Pedology is the
study of soil as a natural bodyand does not focus on the soil’s immediate practical use. A pedologiststudies, examines and classifies soilas they occur in their natural environment. - Edaphological Approach: Edaphology (from Greek word edaphos, means soil or ground) is the study of soil from the stand point of higher plants. Edaphologists consider the various properties of soil
in relation to plant production. They are practical and have the production of food and fibre as their ultimate goal. They must determine the reasons for variation in the productivity of soils and find means for improvement.
“The science dealing with soil as a natural resource on the surface of the earth, including Pedology (soil genesis, classification and mapping), physical, chemical, biological and fertility properties of soil and these properties in relation to their management for crop production.”
👉🏻 Soil Science has six well defined and developed disciplines:
- Soil Fertility → Nutrient supplying properties of soil
- Soil Chemistry → Chemical constituents, chemical properties and the chemical reactions
- Soil Physics → Involves the study of physical properties
- Soil Microbiology → Deals with microorganisms, its population, classification, its role in transformations
- Soil Conservation → Dealing with protection of soil against physical loss by erosion or against chemical deterioration i.e. excessive loss of …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel