🧗🏻 Soil Consistence
Soil Consistence, Crusting, Compaction
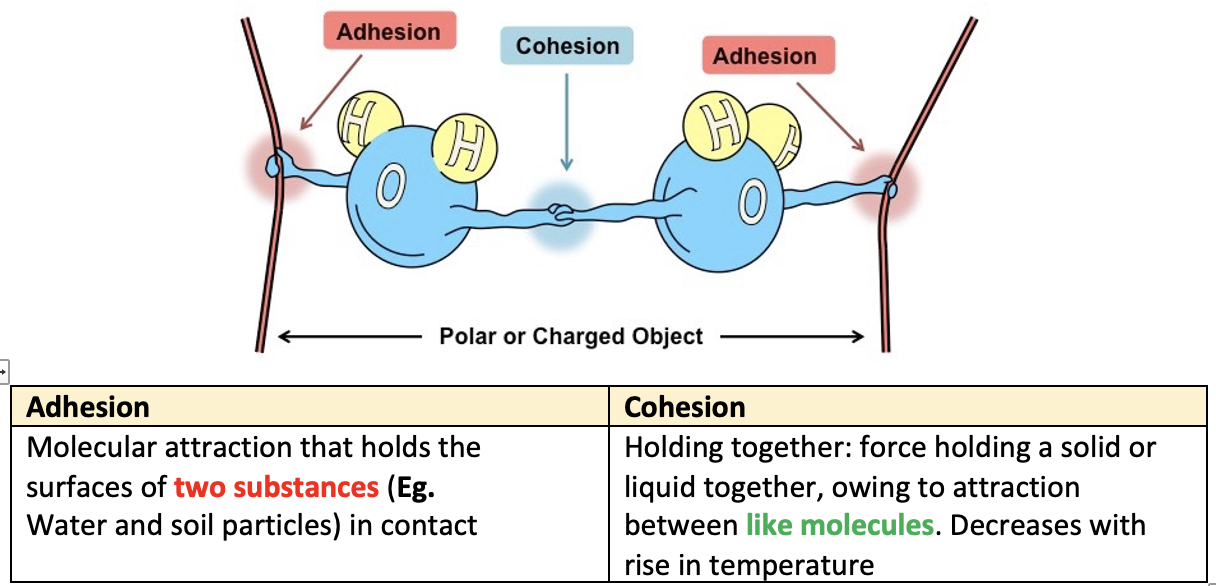
- Soil consistence is defined as “the resistance of a soil at various moisture contents to mechanical stresses or manipulations”.
- It combines both the ‘cohesive’ and ‘adhesive’ forces, which determine the ease with which a soil can be reshaped or ruptures.
1. Wet soils
- Consistency is denoted by terms stickiness and plasticity
- Stickiness is grouped into four categories namely
- non sticky
- slightly sticky
- sticky
- very sticky
- Plasticity of a soil is its capacity to be moulded (to change its shape depending on stress) and to retain the shape even when the stress is removed.
- Soils containing more than about 15% clay exhibit plasticity – pliability and the capacity of being molded. There are four degrees in plasticity namely
- non plastic
- slightly plastic
- plastic
- very plastic
2. Moist soil
- Moist soil with least coherence adheres very strongly and resists crushing between the thumb and forefinger. The different categories are
- Loose-non coherent
- Very friable - coherent, but very easily crushed
- Friable - easily crushed
- Firm - crushable with moderate pressure
- Very firm - crushable only under strong pressure
- Extremely firm - completely resistant to crushing. (type and amount of clay and humus influence this consistency)
3. Dry soil
- In the absence of moisture, the degree of resistance is related to the attraction of particles for each other. The different categories are
- Loose - non coherent
- Soft - breaks with slight pressure and becomes powder
- Slightly hard - break under moderate pressure
- Hard - breaks with difficulty with pressure
- Very hard - very resistant to pressure
- Extremely hard - extreme resistance and cannot be broken
Soil crusting
- Formation Mechanism: Soil crusts usually are formed as a result of compaction at the immediate surface due to an externally applied force. This force is supplied primarily by the impact of raindrops as the soil is wetted and the radiant energy of the sun as the soil dries. When the rain drops fall on dry soil.
- Soil Strength is determined by
penetrometer.

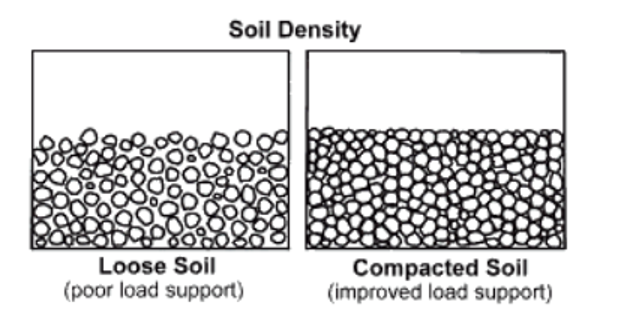
Soil Compaction
- Soil compaction is defined as the method of mechanically increasing the density of soil.
- In construction, this is a significant part of the building process. If performed improperly, settlement of the soil could occur and result in unnecessary maintenance costs or structure failure.
- Almost all types of building sites and construction projects utilize mechanical compaction techniques.
- Soil consistence is defined as “the resistance of a soil at various moisture contents to mechanical stresses or manipulations”.
- It combines both the ‘cohesive’ and ‘adhesive’ forces, which determine the ease with which a soil can be reshaped or ruptures.

1. Wet soils
- Consistency is denoted by terms stickiness and plasticity
- Stickiness is grouped into four categories namely
- non sticky
- slightly sticky
- sticky
- very sticky
- Plasticity of a soil is its capacity to be moulded (to change its shape depending on stress) and to retain the shape even when the stress is removed.
- Soils containing more than about 15% clay exhibit plasticity – pliability and the capacity of being molded. There are four …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel