𝍀 Soil Density
Particle and Bulk Density
Particle Density (Real Specific Gravity)
- The weight per unit
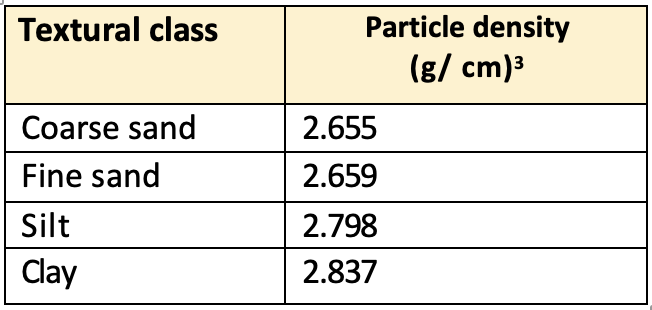
volume of the solid portionof soil is called particle density. - Generally, particle density of normal soils is 2.65 grams per cubic centimeter.
- Particle density depends on the chemical composition and crystal structure of the mineral particle. The particle density is higher if large amount of heavy minerals such as magnetite, limonite and hematite are present in the soil.
- With increase in organic matter of the soil the particle density decreases.
- Particle density is also termed as
true density.
Particle density of different soil textural classes
Bulk Density (Apparent Specific Gravity)
- The oven dry weight of a unit
volume of soil inclusive of pore spacesis called bulk density. - The bulk density of a soil is
always smaller than its particle density. - Bulk density of general soils is taken as 1.33 g / cm3 (Just half of P.D.), whereas that of organic matter is about 0.5.
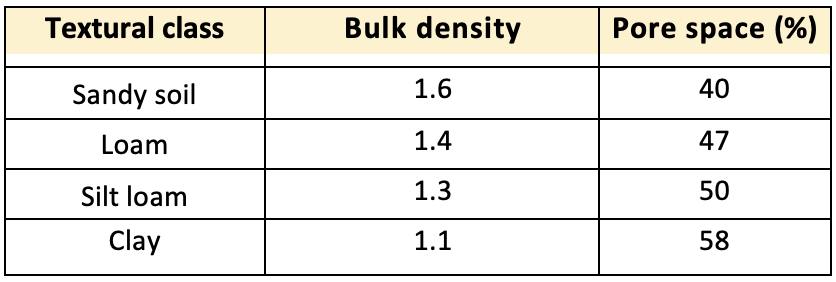
- Bulk density normally decreases, as mineral soils become finer in texture. The bulk density varies indirectly with the total pore space present in the soil and gives a good estimate of the porosity of the soil.
- Bulk density is of greater importance than particle density in understanding the physical behavior of the soil. Generally, soils with low bulk densities have favorable physical conditions.
- Bulk density of different textural classes
⭐️ Factors affecting bulk density
- Pore space: Since bulk density relates to the combined volume of the solids and pore spaces, soils with high proportion of pore space to solids have lower bulk densities than those that are more compact and have less pore space. Consequently, any factor that influences soil pore space will affect bulk density.
- Texture: Fine textured surface soils such as silt loams, clays and clay loams generally have lower bulk densities than sandy soils. This is because the fine textured soils tend to organize in porous grains especially because of adequate organic matter content. This results in high pore space and low bulk density. However, in sandy soils, organic matter content is generally low, the solid particles lie close together and the bulk density is commonly higher than in fine textured soils.
- Organic matter content: More the organic matter content in soil results in high pore space there by shows lower bulk density of soil and vice-versa.
Porosity
- Soil porosity refers to that part of a soil volume that is not occupied by soil particles or organic matter.
- The pore space of a soil is the space occupied by air and water.
⭐️ Factors influencing pore space
-
Soil texture
- In sandy soils, there are 25000 pores/m2 whereas in clay, 25 X 106 pores/ m2.
-
Crops / vegetation
- Some crops like blue grass increases the porosity to 57.2% from the original 50%.
- Cropping reduces the porosity as cultivation reduces the organic matter content and hence decrease in granulation.
- Virgin soils have more pore space. Continuous cropping reduces pore space than intermittent cropping. More the number of crops per year, lesser will be the pore space particularly macro pores.
- Conservation tillage and no tillage reduces porosity than conventional tillage.
-
Size of pores

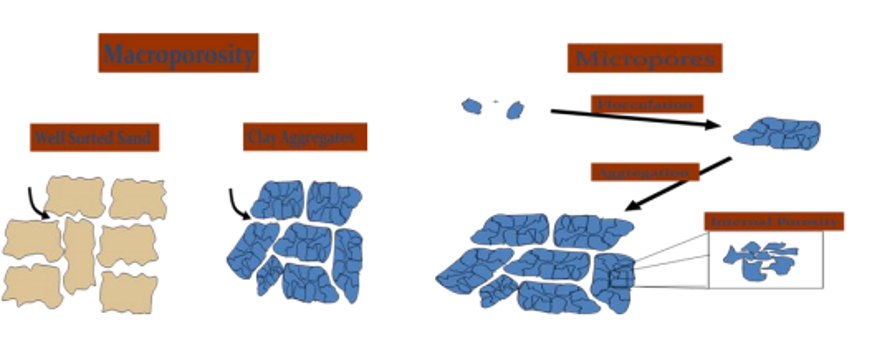
- In macro pores, air and water moves freely due to gravitation and mass flow. In micro pores, the movement of air and water is very slow and restricted to capillary movement and diffusion.
- Sandy soil have more macro pores and clay soils have more micro pores. So in sandy soils, water and air movement is rapid due to macro pores though the pore space are less.
- Clay soils the air and water is slower due to micro pores though the total pore space is higher.
- Loamy soils will have 50% porosity and have equal portion of macro and micro pores.
Significance and manipulation of soil porosity
- The bulk density and pore space are inter related. Development of low bulk density values also means the development of large amount of pore spaces.
- In nature, low bulk density values are usually found in soils with high organic matter contents. High biological activities are necessary for formation and large accumulation of organic matter. Together with the effect of soil organisms, the high humus content will encourage aggregation, increasing in this way soil porosity, and thereby decreasing bulk density values.
- The cultivation effect of the soil macro and micro fauna produces an intricate system of macropores, which is a major factor for lowering the bulk density of soil. Continuous cropping is noted to decrease the amount of organic matter in soils, and is expected to decrease soil aggregation.
- Tillage by ploughing is designed to increase the pore space in soils, but is in fact decrease organic matter. To alleviate these problems conservation tillage and no tillage have been introduced. Though many claimed that this increased the organic matter, the later have not always increased the total pore space.
Particle Density (Real Specific Gravity)
- The weight per unit
volume of the solid portionof soil is called particle density. - Generally, particle density of normal soils is 2.65 grams per cubic centimeter.
- Particle density depends on the chemical composition and crystal structure of the mineral particle. The particle density is higher if large amount of heavy minerals such as magnetite, limonite and hematite are present in the soil.
- With increase in organic matter of the soil the particle density decreases.
- Particle density is also termed as
true density.
Particle density of different soil textural classes

Bulk Density (Apparent Specific Gravity)
- The oven dry weight of a unit
volume of soil inclusive of pore spacesis called bulk density. - The bulk density of a soil is
always smaller …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel