💰 Budget
Budget 2024-25, 7 Budget Priorities, and all important annoncements
- Despite global economy remaining under the grip of policy uncertainties, India’s economic growth continues to be the shining exception and will remain so in the years ahead.
- Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt Nirmala Sitharaman, while presenting the Union Budget 2024-25 in Parliament said that India’s inflation continues to be low, stable and moving towards the 4 per cent target. Core inflation (non-food, non-fuel) currently is 3.1 per cent and steps are being taken to ensure supplies of perishable goods reach market adequately.
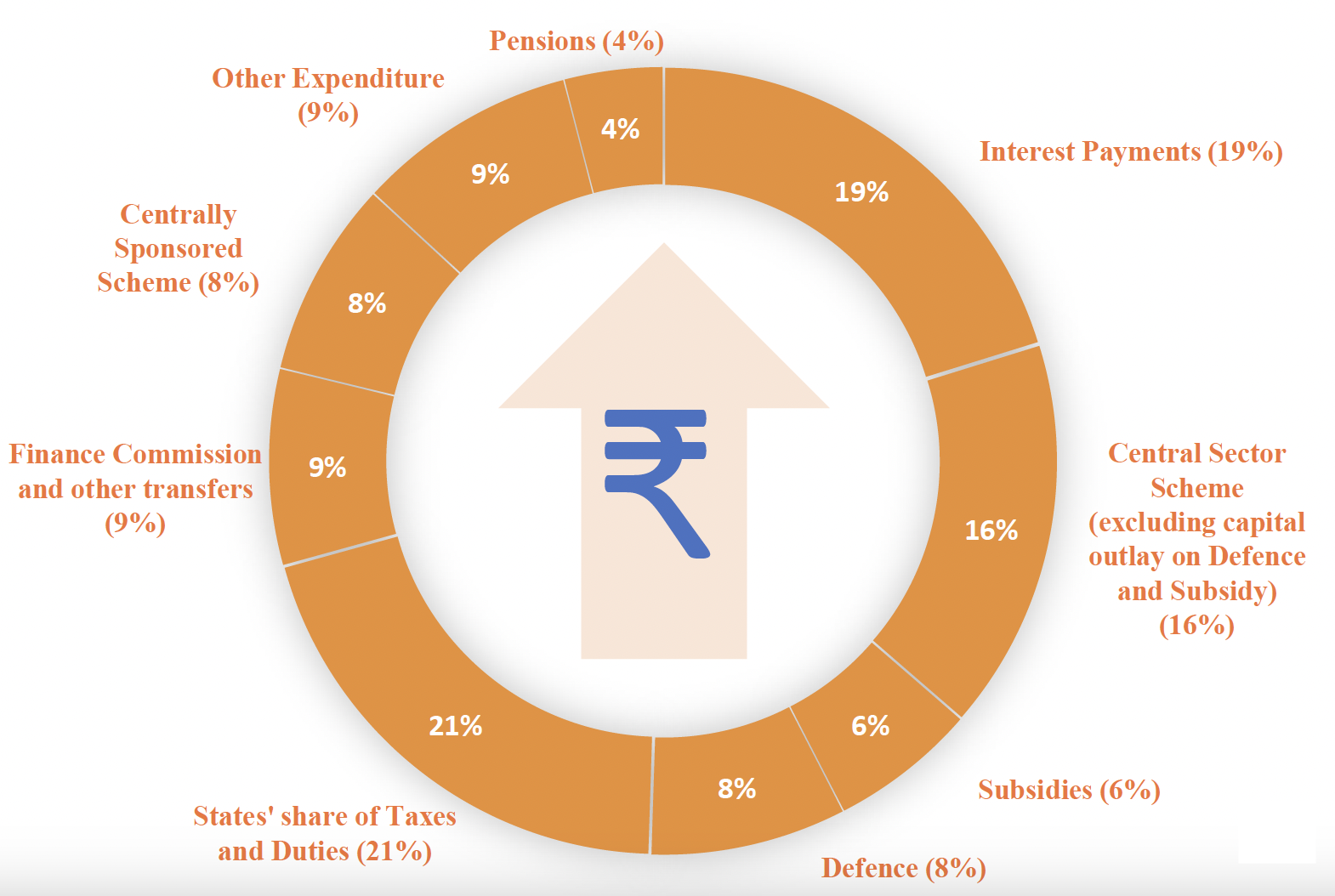
- The Finance Minister informed that for the year 2024-25, the total receipts other than borrowings and the total expenditure are estimated at ₹32.07 lakh crore and ₹48.21 lakh crore respectively.
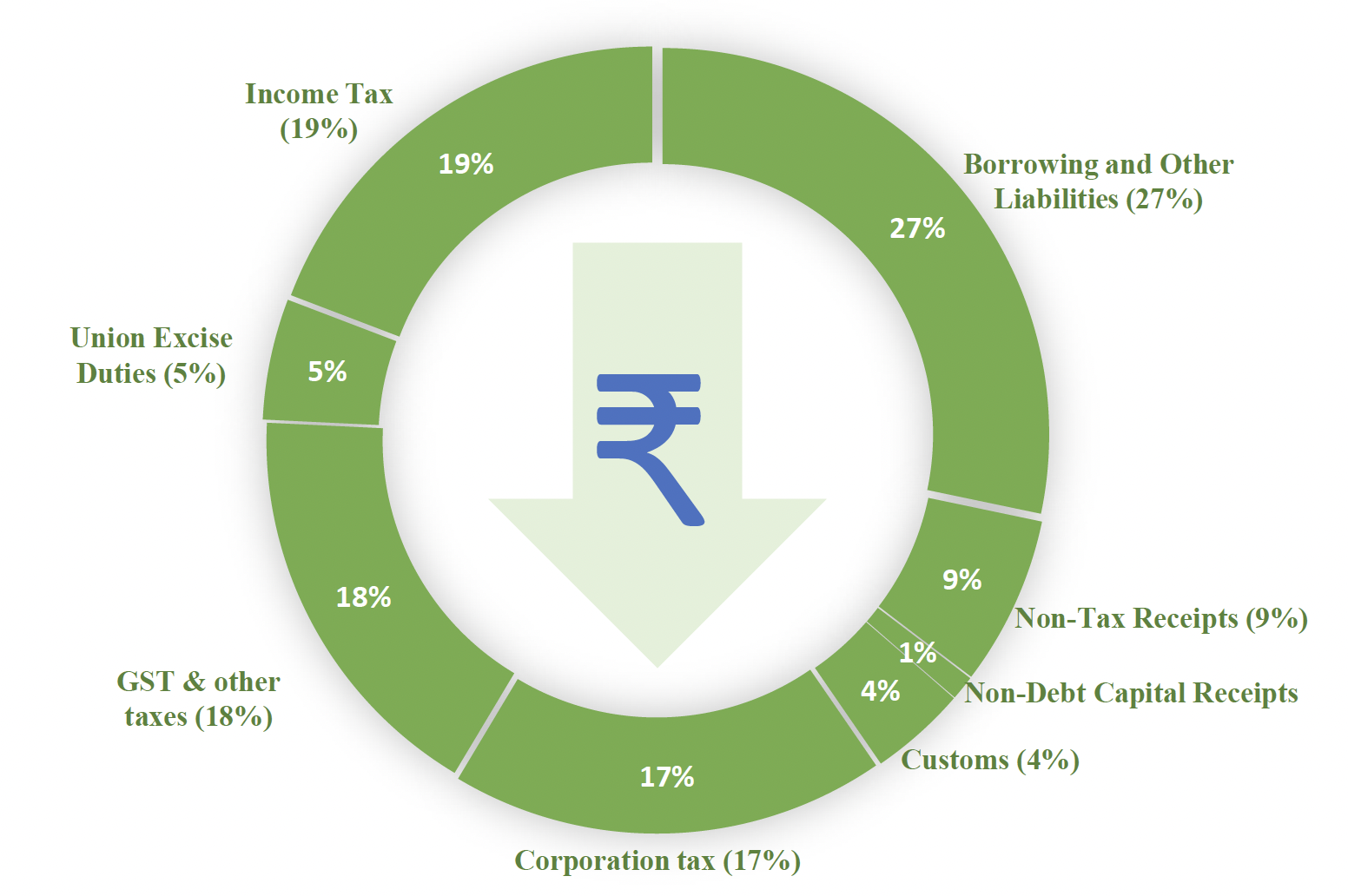
Each Rupee Comes From
Each Rupee Goes To
- The net tax receipts are estimated at ₹25.83 lakh crore and the fiscal deficit is estimated at
4.9 per cent of GDP(Current fiscal deficit, 2024). - She said, the gross and net market borrowings through dated securities during 2024-25 are estimated at ₹14.01 lakh crore and ₹11.63 lakh crore respectively.
- Smt Sitharaman emphasised that the fiscal consolidation path announced by her in 2021 has served economy very well, and the government will aim to reach a deficit below 4.5 per cent next year.
- India grew at
8.2%in FY 2024. - The Gross Non-performing asset (GNPA) ratio of scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) now stands at
2.8%, a reduction from 3.8 per cent a year ago.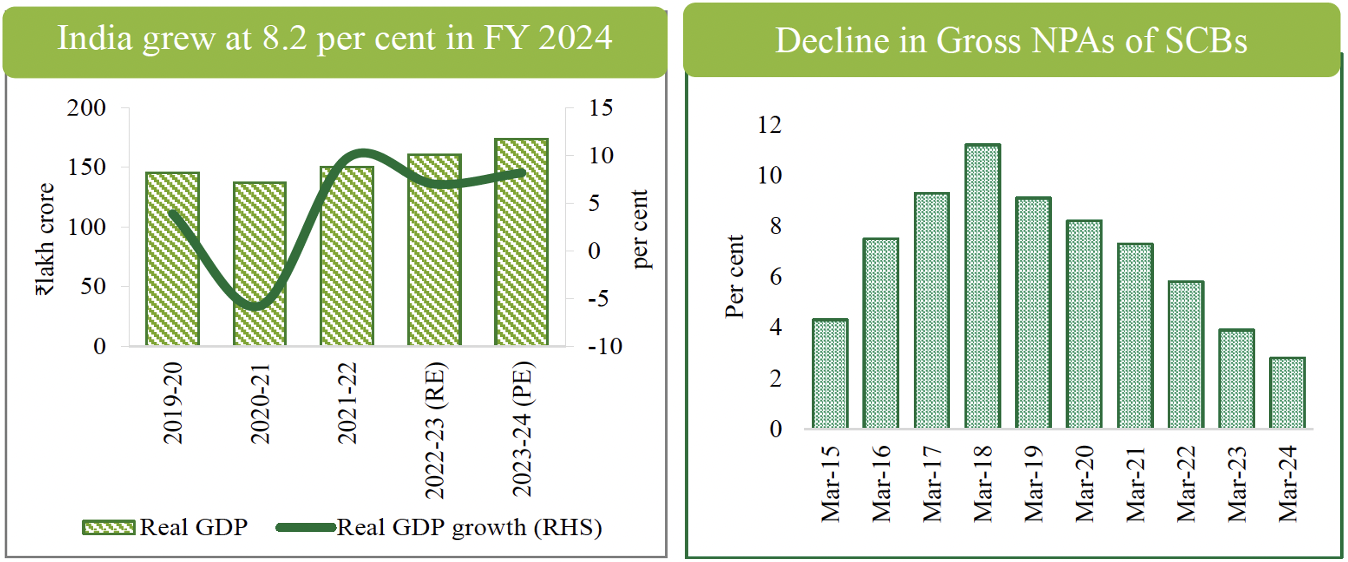
Interim Budget
- The Finance Minister said that the focus is on 4 major castes, namely ‘Garib’ (Poor), ‘Mahilayen’ (Women), ‘Yuva’ (Youth) and ‘Annadata’ (Farmer).
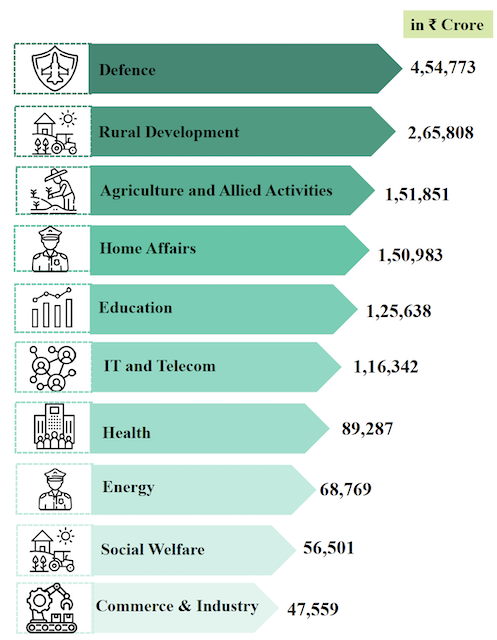
Major Expanditure
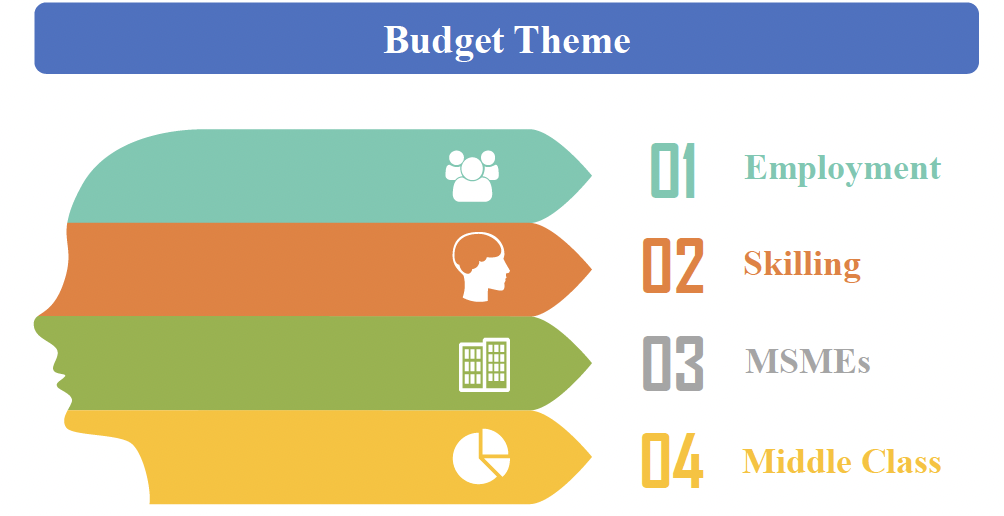
Budget Theme
- Dwelling on the Budget theme, Smt Sitharaman said, turning attention to the full year and beyond, in this budget, we particularly focus on employment, skilling, MSMEs, and the middle class.
- She announced the Prime Minister’s package of 5 schemes and initiatives to facilitate employment, skilling and other opportunities for 4.1 crore youth over a 5-year period with a central outlay of ₹2 lakh crore. This year, ₹1.48 lakh crore has been allocated for education, employment and skilling.
Budget Priorities
The Finance Minister said, for pursuit of ‘Viksit Bharat’, the budget envisages sustained efforts on the following 9 priorities for generating ample opportunities for all.
- Productivity and resilience in Agriculture
- Employment & Skilling
- Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
- Manufacturing & Services
- Urban Development
- Energy Security
- Infrastructure
- Innovation, Research & Development and
- Next Generation Reforms
Priority 1: Productivity and resilience in Agriculture
- The Finance Minister announced that the government will undertake a comprehensive review of the agriculture research setup to bring the focus on raising productivity.
- New
109high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops will be released for cultivation by farmers. - In the next two years,
1 crore farmersacross the country will be initiated into natural farming supported by certification and branding. 10,000need-based bio-input resource centres will be established.- For achieving self-sufficiency in pulses and oilseeds, government will strengthen their production, storage and marketing and to achieve ‘atmanirbharta’ for oil seeds such as mustard, groundnut, sesame, soybean, and sunflower.
- Government, in partnership with the states, will facilitate the implementation of the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in agriculture for coverage of farmers and their lands in 3 years. Digital crop survey for Kharif using OPI to be taken up in 400 districts.
- Issuance of Jan Samarth based Kisan Credit Cards to be enabled in 5 states.
- Smt Sitharaman announced a provision of
₹1.52 lakh crorefor agriculture and allied sector this year. - ₹86,000 crore for MGNREGA.
- Transforming Agriculture Research: Comprehensive review of the agriculture research setup to bring focus on raising productivity and developing climate resilient varieties.
- Shrimp Production & Export: Financing for Shrimp farming, processing and export will be facilitated through NABARD. Financial support for setting up a network of Nucleus Breeding Centres for Shrimp Broodstocks to be provided.
- National Cooperation Policy: National Cooperation Policy to be framed with an objective to Fast-tracking growth of rural economy & generation of employment opportunities. For systematic, orderly and all-round development of the cooperative sector.
- Vegetable production & supply chain: Promotion of FPOs, cooperatives & start-ups for vegetable supply chains for collection, storage, and marketing.
Priority 2: Employment & Skilling
- The Finance Minister said that the government will implement 3 schemes for ‘Employment Linked Incentive’, as part of the Prime Minister’s package. These will be based on enrolment in the EPFO, and focus on recognition of first-time employees, and support to employees and employers.
- Scheme 1st: First Timers
- Direct benefit transfer of
1-month salaryto new entrants in all formal sectors in 3 installments up to ₹15,000 to first-time employees registered in EPFO. - Expected to benefit 210 lakh youth.
- Direct benefit transfer of
- Scheme 2nd: Job Creation in Manufacturing
- Incentive to be provided directly to both employee and employer as per their EPFO contribution, in the first 4 years of employment.
- Linked to first time employees.
- Expected to benefit 30 lakh youth.
- Scheme 3rd: Support to Employers
- Reimbursement to employers up to ₹3,000 per month for 2 years towards their EPFO contribution for each additional employee.
- Expected to generate 50 lakh jobs.
- Scheme 4th: Referring to the Skilling programme, the Finance Minister announced a new centrally sponsored scheme, as the 4th scheme under the Prime Minister’s package, for skilling in collaboration with state governments and Industry.
20 lakh youthwill be skilled over a 5-year period and 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) will be upgraded in hub and spoke arrangements with outcome orientation.- Course content & design aligned as per skill needs of industry.
- Scheme 5th: Internship in Top Companies
- The Finance Minister said that as the 5th scheme under the Prime Minister’s package, government will launch a comprehensive scheme for providing internship opportunities in 500 top companies to 1 crore youth in 5 years.
- The internship will be conducted for a duration of
12 months, and a stipend of₹5,000 per monthalong with a one-time assistance of ₹6,000 through the CSR funds will be provided .
- Government will also facilitate higher participation of women in the workforce through setting up of working women hostels in collaboration with industry, and establishing creches.
- She also announced that the
Model Skill Loan Schemewill be revised to facilitate loans up to ₹7.5 lakh with a guarantee from a government promoted Fund, which is expected to help 25,000 students every year. - For helping the youth, who have not been eligible for any benefit under government schemes and policies, she announced a financial support for
loans upto ₹10 lakhfor higher education in domestic institutions.E-vouchersfor this purpose will be given directly to 1 lakh students every year for annual interest subvention of 3 per cent of the loan amount.
Priority 3: Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
- Finance Minister emphasised that implementation of schemes meant for supporting economic activities by craftsmen, artisans, self-help groups, scheduled caste, schedule tribe and women entrepreneurs, and street vendors, such as PM Vishwakarma, PM SVANidhi, National Livelihood Missions, and Stand-Up India will be stepped up.
- Purvodaya: Vikas bhi Virasat bhi
- Government will formulate a plan, Purvodaya, for the all-round development of the eastern region of the country covering Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh. This will cover human resource development, infrastructure, and generation of economic opportunities to make the region an engine to attain Viksit Bharat.
- Amritsar Kolkata Industrial Corridor with development of an industrial node at Gaya.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan (PM JUGA): The Finance Minister announced that for improving the socio-economic condition of tribal communities, government will launch the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan by adopting saturation coverage for tribal families in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts covering 63,000 villages and benefitting 5 crore tribal people.

- More than 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank will be set up in the North East region to expand the banking services.
- A provision of
₹2.66 lakh crorefor rural development including rural infrastructure was made this year. Rs 3 lakh crorefor schemes benefitting women and girls.- Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act:
- Financial support of ₹15,000 crores will be arranged in FY 24-25.
- Completion of Polavaram Irrigation Project to ensure food security of the nation. The Polavaram Project is an under construction multi-purpose irrigation project on the Godavari River in the Eluru District and East Godavari District in Andhra Pradesh.
- Funds to be provided for essential infrastructure development in Kopparthy node on Vishakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor & Orvakal node on Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
Priority 4: Manufacturing & Services
- Support for promotion of MSMEs:
- Smt Sitharaman said, this budget provides special attention to MSMEs and manufacturing, particularly labour-intensive manufacturing.
- A separately constituted self-financing guarantee fund will provide, to each applicant, guarantee cover up to ₹100 crore, while the loan amount may be larger.
- Similarly, Public sector banks will build their in-house capability to assess MSMEs for credit, instead of relying on external assessment.
- She also announced a new mechanism for facilitating continuation of bank credit to MSMEs during their stress period.
- Mudra Loans: The limit of Mudra loans will be enhanced to
₹20 lakhfrom the current ₹ 10 lakh for those entrepreneurs who have availed and successfully repaid previous loans under the ‘Tarun’ category. - MSME Units for Food Irradiation, Quality & Safety Testing:
- Financial support for setting up of 50 multi-product food irradiation units in the MSME sector will be provided.
- Setting up of 100 food quality and safety testing labs with NABL accreditation will also be facilitated.
- To enable MSMEs and traditional artisans to sell their products in international markets, E-Commerce Export Hubs will be set up in public-private-partnership (PPP) mode.
- Turnover threshold of buyers for mandatory onboarding on TReDS platform to be reduced from ₹500 Cr to ₹250 Cr.
- E-Commerce Export Hubs to be set up in PPP mode to enable MSMEs & traditional artisans to sell their products in international markets.
- Twelve industrial parks under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme.
- Rental housing with dormitory type accommodation for industrial workers in PPP mode with VGF support.
Priority 5: Urban Development
- Urban Housing: Under the PM AwasYojana Urban 2.0, housing needs of
1 crore urban poor and middle-class familieswill be addressed with an investment of ₹10 lakh crore. This will include the central assistance of ₹2.2 lakh crore in the next 5 years. - Enabling policies and regulations for efficient and transparent rental housing markets with enhanced availability will also be put in place.
- Water Supply and Sanitation: In partnership with the State Governments and Multilateral Development Banks, government will promote water supply, sewage treatment and solid waste management projects and services for 100 large cities through bankable projects.
- PM SVANidhi: Building on the success of PM SVANidhi Scheme in transforming the lives of street vendors, Government envisions a scheme to support each year, over the next five years, the development of 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs in select cities.
- 14 large cities with a population above 30 lakh will have Transit Oriented Development Plans.
- Encouraging states to lower stamp duties for properties purchased by women.
Priority 6: Energy Security
- In line with the announcement in the interim budget,
PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana (PM SGMBY)has been launched to install rooftop solar plants to enable1 crore householdsobtain free electricity up to 300 units every month. The scheme has generated remarkable response with more than 1.28 crore registrations and 14 lakh applications.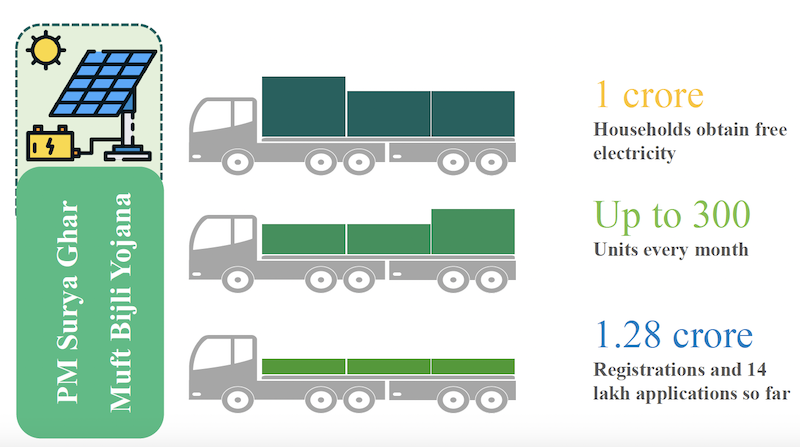
- Nuclear energy is expected to form a very significant part of the energy mix for Viksit Bharat. Setting up Bharat Small Reactors.
- Pumped Storage Policy to be brought out for electricity storage and integration of renewable energy in the overall energy mix R&D of small and modular nuclear reactors and newer technologies for nuclear energy
- Joint venture between NTPC and BHEL to set up a full scale 800 MW commercial thermal plant using AUSC technology Roadmap for ‘hard to abate’ industries to be formulated for transition from ‘Perform, Achieve and Trade’ mode to ‘Indian Carbon Market’ mode.
- Energy Audit: Energy audit of traditional micro and small industries in 60 clusters with financial support for shifting them to cleaner forms.
Priority 7: Infrastructure
- The Finance Minister underlined that significant investment the Central Government has made over the years in building and improving infrastructure has had a strong multiplier effect on the economy.
- Government will endeavour to maintain strong fiscal support for infrastructure over the next 5 years, in conjunction with imperatives of other priorities and fiscal consolidation.
₹11,11,111 crorefor capital expenditure has been allocated this year, which is3.4 per cent of our GDP.- 21.5 lakh crore provision for long-term interest-free loans to support Infrastructure investment by state governments.
- Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme: For Irrigation and Flood Mitigation in Bihar, through the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme and other sources, government will provide financial support for projects with estimated cost of ₹11,500 crore such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and 20 other ongoing and new schemes including barrages, river pollution abatement and irrigation projects.
- Assistance to Assam & Himachal Pradesh for flood management and for Uttarakhand & Sikkim for losses due to cloud bursts, flash floods and landslides.
- Pradhan Mantri Gram SadakYojana (PMGSY): The Finance Minister announced that
Phase IVof PMGSY will be launched to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations which have become eligible in view of their population increase. - Tourism
- Development of Vishnupad Temple Corridor and Mahabodhi Temple Corridor modelled on Kashi Vishwanath Temple Corridor.
- Comprehensive development initiative for Rajgir will be undertaken which holds religious significance for Hindus, Buddhists and Jains.
- The development of Nalanda as a tourist centre besides reviving Nalanda University to its glorious stature.
- Assistance to development of Odisha’s scenic beauty, temples, monuments, craftsmanship, wildlife sanctuaries, natural landscapes and pristine beaches making it an ultimate tourism destination.
Priority 8: Innovation, Research & Development
- The Finance Minister said that government will operationalize the Anusandhan National Research Fund for basic research and prototype development and set up a mechanism for spurring private sector-driven research and innovation at commercial scale with a financing pool of ₹1 lakh crore in line with the announcement in the interim budget.
- Space Economy: With our continued emphasis on expanding the space economy by 5 times in the next 10 years, a venture capital fund of ₹1,000 crore will be set up.
Priority 9: Next Generation Reforms
- Economic Policy Framework: The Finance Minister said that the government will formulate an Economic Policy Framework to delineate the overarching approach to economic development and set the scope of the next generation of reforms for facilitating employment opportunities and sustaining high growth.
- Technology to speed up digitalization of economy.
- Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0 to improve Ease of Doing Business.
- States to be incentivized to implement Business Reforms Action.
- Plans and digitalization.
- Sectoral databases for improving data governance and management.
- Rural & Urban land related actions:
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands.
- Survey of map sub-divisions as per current ownership.
- Linkages to the farmers’ registries.
- Land records in urban areas will be digitized with GIS mapping.
- Digitization of cadastral maps.
- Establishment of land registry.
- Labour related reforms:
- Government will facilitate the provision of a wide array of services to labour, including those for employment and skilling.
- A comprehensive integration of E-shram portal with other portals to provide one-stop labour services solution; will include mechanism to connect job-seekers with potential employers and skill providers.
- Shram Suvidha and Samadhan portals will be revamped to enhance ease of compliance for industry and trade.
- NPS Vatsalya: NPS-Vatsalya, a plan for contribution by parents and guardians for minors will be started. On attaining the age of majority, the plan can be converted seamlessly into a normal NPS account.
- New Pension Scheme (NPS): The Finance Minister said that the Committee to review the NPS has made considerable progress in its work and a solution will be evolved which addresses the relevant issues while maintaining fiscal prudence to protect the common citizens.
- Government will develop a taxonomy for climate finance for enhancing the availability of capital for climate adaptation and mitigation.
- Foreign Direct Investment and Overseas Investment: The rules and regulations for Foreign Direct Investment and Overseas Investments will be simplified to
- facilitate foreign direct investments,
- nudge prioritization, and
- promote opportunities for using Indian Rupee as a currency for overseas investments.
Tax Related Reforms
- Apart from giving relief to four crore salaried individuals and pensioners of the country in the direct taxes, Union Budget 2024-25 seeks to comprehensively review the direct and indirect taxes in the next six months, simplifying them, reducing tax incidence and compliance burdens and broadening the tax nets.
- The Budget proposes comprehensive rationalization of GST tax structure along with review of the Custom Duty rate structure to improve the tax base and support domestic manufacturing.
- To promote investment and foster employment, Budget has given boost to entrepreneurial spirit and start-up ecosystem, abolishing angel tax for all classes of investors.
- Corporate tax rate on foreign companies reduced from 40 to
35 per centto attract foreign capital. - A comprehensive review of Income – Tax Act is targeted at reducing disputes and litigations and to make the act lucid, concise and easy to read.
- Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that simplification of tax regimes without exemptions and deductions for corporate and personal income tax has been appreciated by tax payers as over 58 per cent of corporate tax came from simplified tax regime in 2022-23 and more than two third tax payers have switched over to the new personal income tax regime.
- Further, a simpler tax regime for foreign shipping companies operating domestic cruises is proposed looking at the tremendous potential of cruise tourism.
- Foreign mining companies selling raw diamonds in the country can now benefit from safe harbor rates which will benefit the diamond industry.
- Income-tax Act, 1961 to be made concise and easy to read.
- Time limit for search cases to be reduced from 10 years to 6 years before year of search.
- Short-term gains on certain financial assets to be taxed at
20%. - Long-term gains on all financial and non-financial assets to be taxed at
12.5%, increased from 10%. - Limit of exemption of capital gains has been increased to
₹1.25 Lakhper year to benefit lower and middle-income classes. - Listed financial assets held for more than a year and unlisted assets (financial and non-financial) held for more than two years to be classified as long term assets. Unlisted bonds and debentures, debt mutual funds and market linked debentures will continue to attract applicable capital gains tax.
- Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme, 2024 for resolution of certain income tax disputes pending in appeal.
- Budget 2024-25 increased standard deduction of salaried employees from ₹ 50,000/- to
₹ 75,000/-for those opting for new tax regime. - Similarly, deduction on family pension for pensioners enhanced from ₹ 15,000/- to ₹ 25,000/-.
- Assessments now, can be reopened beyond three years up to 5 years from end of year of assessment, only if, the escaped income is more than ₹ 50 Lakh.
- The new tax regime rate structure is also revised to give a salaried employee benefits up to ₹ 17,500/- in income tax.
| Income Slabs | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 – 3 Lakh rupees | NIL |
| 3 – 7 Lakh rupees | 5 per cent |
| 7 – 10 Lakh rupees | 10 per cent |
| 10 – 12 Lakh rupees | 15 per cent |
| 12 – 15 Lakh rupees | 20 per cent |
| Above 15 Lakh rupees | 30 per cent |
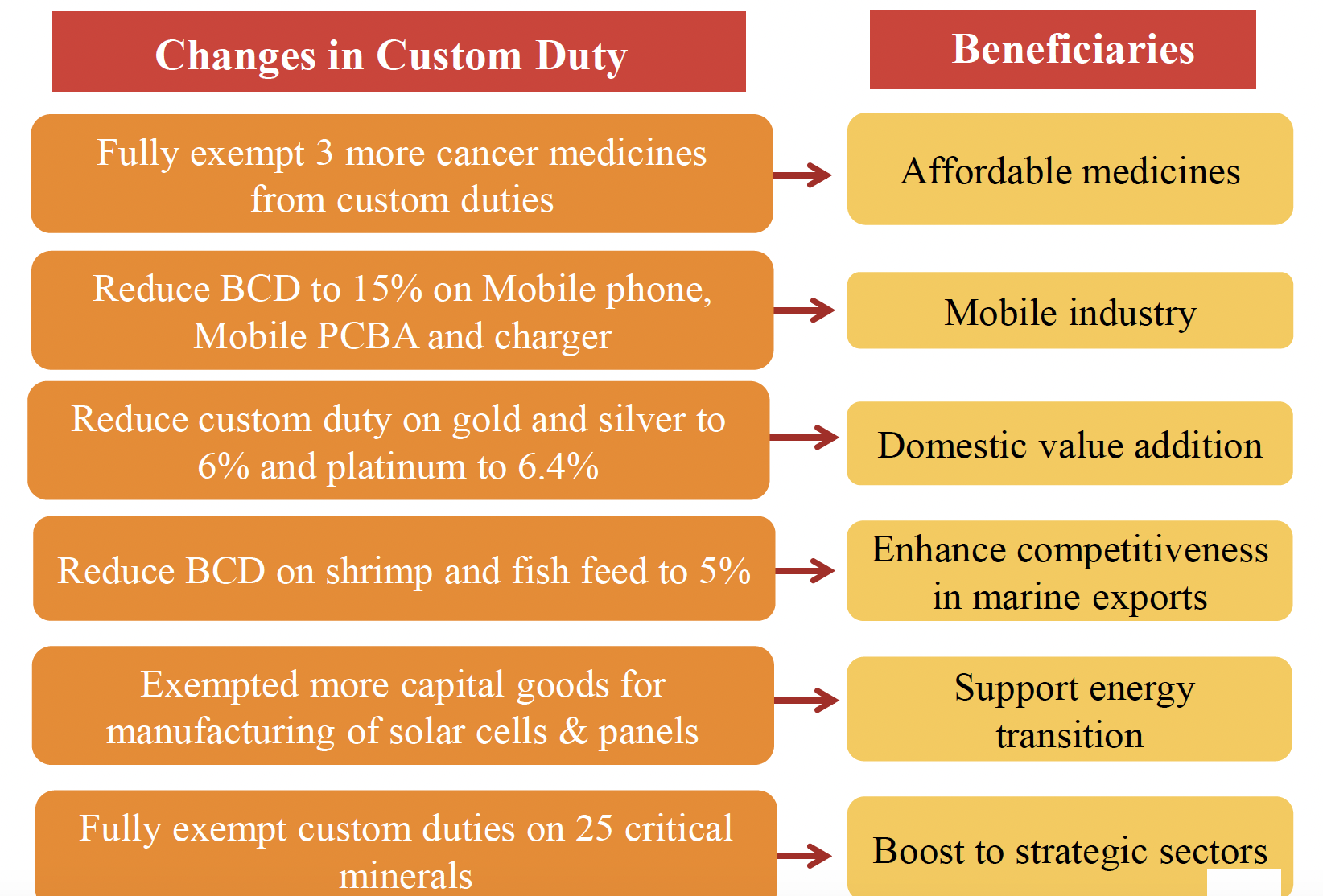
Sector Specific Customs Duty Proposals
- Giving relief to cancer patients, Budget fully exempted three more cancer treating medicines from custom duties, namely, Trastuzumab Deruxtecan, Osimertinib and Durvalumab.
- There will be reduction in Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on X-ray machines tubes and flat panel detectors. BCD on mobile phones, Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) and mobile chargers reduced to 15 per cent.
References
- https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/
- https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2035618
- Wikipedia