🔬 Cytoplasmic Inheretance
Features, Applications, Difference
Cytoplasmic or Extra nuclear Inheritance
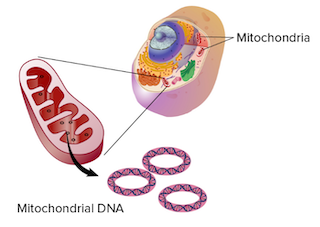
- The inheritance of almost all traits or characters from generation to generation is governed by the genes of nuclear chromosomes. But the inheritance of some traits is also governed by the cytoplasm.
- Since major part of the cytoplasm of the zygote is derived from the female gamete and male gametes carry little or no cytoplasm means this inheritance is governed by female parent. The inheritance of the traits governed by the cytoplasm or female parent or extra nuclear chromosomes is called Cytoplasmic/Maternal/Extranuclear inheritance.
- Genes/DNA/Chromosomes are also present in the Cytoplasmic organelles, like chloroplasts & mitochondria are solely responsible for the cytoplasmic inheritance. Genes present in the cytoplasm are called plasmogenes or plasmones.
Features of Cytoplasmic Inheritance
- In the inheritance of the nuclear genes, male & female parent contribute equally to the progeny and its reciprocal crosses between the parents, yield progenies of the identical phenotype except for sex-linked genes. But in the cytoplasmic inheritance only maternal effect appear in the progeny because eggs or ova (female gametes) contribute large amount of cytoplasm and many extra nuclear genes in the form of inactive mRNA, rRNA & tRNA and also in the form of DNA of mitochondria, chloroplasts & endosymbionts. Therefore reciprocal crosses yield different results (non Mendelian).
- Certain traits of F1, F2 or F3 progeny are not the expression of their own genes, but rather those of the maternal parents. The substance which produce the maternal effects are transcriptional products i.e. mRNA, rRNA, tRNA.
- Inheritance of some characters like male sterility in maize is governed by mitochondrial DNA. This maternal inheritance of male sterility was discovered by Rhoades (1933) in Maize.
- Plastid inheritance in Four O’clock plant, Mirabilis jalapa was discovered by C. Correns (1908). He found the colour of leaf was totally governed by the colour of the female parent.
- Jenkens (1924) discovered iojap colour (not full developed colour) in leaves of Maize (corn).
- Inheritance of Kappa particles in Paramecium was discovered by Soneberg (1943).
- Ruthsanger (1960) discovered the uniparental (♀ parent) inheritance of streptomycin resistance in chlamydomonas (unicellular green algae
Ethydium bromidehas a capacity to mutate only cytoplasmic genes. Mutation caused by such chemical is heritable which showed the evidence for cytoplasmic inheritance.
Practical application of cytoplasmic inheritance
- It plays an important role in the biology of several organism.
- Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) lines have been developed in several crops viz. maize, pearl millet, sorghum, cotton etc. Hybrid maize seed may be produced without de-tasselling (removal of tassel) by utilizing cytoplasmic/cytoplasmic genetic male sterility.
- It plays key role in mapping of chloroplast and mitochondrial genome in several species viz. yeasts, chlamydomonas, maize etc.
- Role of mitochondria in the manifestation of heterosis is gaining importance.
- Mutation of chloroplast DNA & mitochondrial DNA leads to generation of new variants.
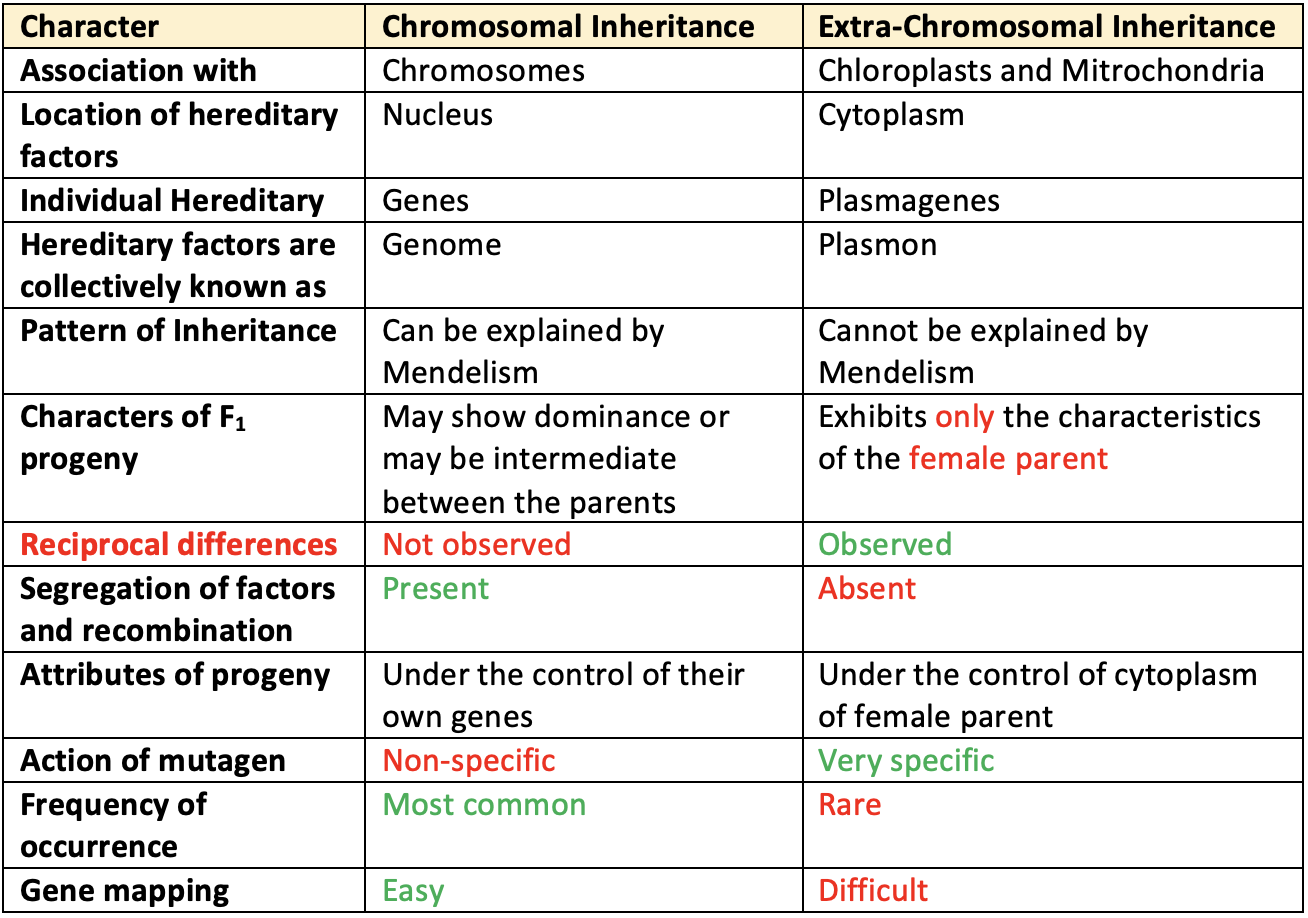
Difference
👉🏻 Between Chromosomal (Nuclear) and Extra-Chromosomal (Cytoplasmic or Extra-Nuclear or Maternal) Inheritance
Cytoplasmic or Extra nuclear Inheritance

- The inheritance of almost all traits or characters from generation to generation is governed by the genes of nuclear chromosomes. But the inheritance of some traits is also governed by the cytoplasm.
- Since major part of the cytoplasm of the zygote is derived from the female gamete and male gametes carry little or no cytoplasm means this inheritance is governed by female parent. The inheritance of the traits governed by the cytoplasm or female parent or extra nuclear chromosomes is called Cytoplasmic/Maternal/Extranuclear inheritance.
- Genes/DNA/Chromosomes are also present in the Cytoplasmic organelles, like chloroplasts & mitochondria are solely responsible for the cytoplasmic inheritance. Genes present in the cytoplasm are called …