⚤ Sex Genetics
Sex linked, Sex influenced, Sex limited traits
Sex linked, Sex influenced & Sex limited traits
- In monoecious/hermaphrodite/bisexual (male & female on the same individual) individuals, the character or trait of the F1 generation is always irrespective of their gender. But in dioecious (male & female on the other individual) individuals there may be two types of traits:
- Some traits do not show any differences in the reciprocal crosses i.e. A♀ x B ♂, B♀ x A ♂
- Some traits show the differences in reciprocal crosses.
- Such traits which do not show any differences in the reciprocal crosses; are located on the autosomes and the traits which show the differences are either located on sex chromosomes or if located on the autosomes, are influenced by or depend on the sex of the individual which carries it.
- The traitses which are located on sex chromosomes are called
sex linked traits. - The traits whose expression is governed or influenced by the sex (maleness or femaleness) of the individual are called
sex influenced traits. - The traits whose expression is dependent on the sex (♂ or ♀) of the individual who carries it, are called
sex limited traits. Such trait is expressed in one sex only and not in the other.
Sex linked traits
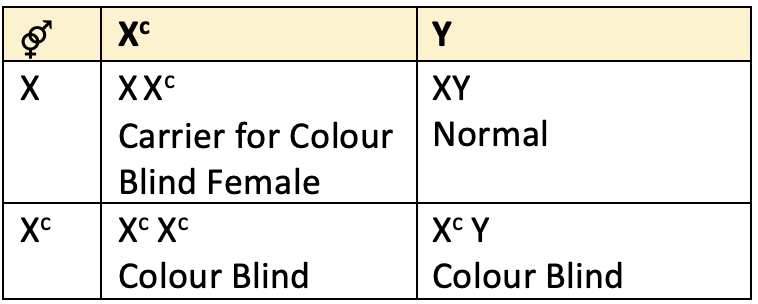
- Example: Colour blindness and haemophilia in human beings.
- Colour blind man is unable to differentiate between red colour and green colour. The gene for red-green colour blindness is located on
X-chromosome.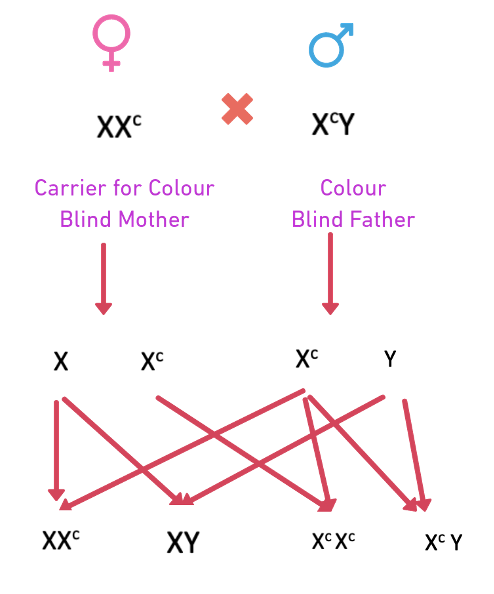
- In hemophilia, the man lacks the factor responsible for blood clotting. Therefore even a minor cut may cause prolonged bleeding leading to death.
- Such traits are transferred from mother to the son and never from the father to the son because they are
X-linkedandrecessivein character - A carrier woman transmits these diseases to the 50% of her sons, even if the father is normal.

Non-disjunction of sex chromosomes
- Nondisjunction means the absence of separation of two homologous X-chromosomes (in Drosophila) during anaphase I of meiosis. In such case, both X-chromosomes go together to the same pole and other pole will get no X-chromosome.
- In 1916,
C.B. Bridgesreported it in Drosophila. - It is a rare phenomenon.
Sex-influenced traits
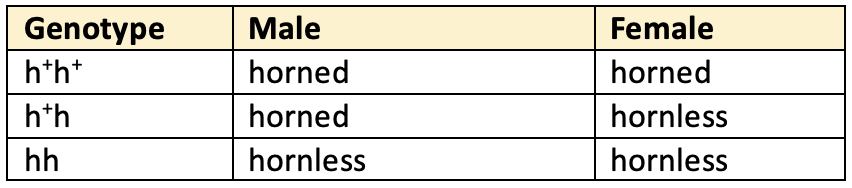
- In some organisms, some characters are influenced by the sex of the organism.
- For example horns in sheep. Horned character is dominant in male but recessive in female.
- This influence is believed to be mainly due to male & female hormones.
Sex limited traits
- E.g.
- Premature baldness is expressed only in the presence of a certain level of male hormone (androgenic).
- Milk production is also sex limited trait. In such cases genes for the particular traits are carried by both male & female.
Sex linked, Sex influenced & Sex limited traits
- In monoecious/hermaphrodite/bisexual (male & female on the same individual) individuals, the character or trait of the F1 generation is always irrespective of their gender. But in dioecious (male & female on the other individual) individuals there may be two types of traits:
- Some traits do not show any differences in the reciprocal crosses i.e. A♀ x B ♂, B♀ x A ♂
- Some traits show the differences in reciprocal crosses.
- Such traits which do not show any differences in the reciprocal crosses; are located on the autosomes and the traits which show the differences are either located on sex chromosomes or if located on the autosomes, are influenced by or depend on the sex of the individual which carries it.
- The traitses which are …