🧜🏼♀️ Center of Origin
Vavilov centers of Origin, Law of homologous series
- A center of origin (or center of diversity) is a geographical area where a group of organisms, either domesticated or wild, first developed its distinctive properties.
- They are also considered
centers of diversity. - Centers of origin were first identified in 1924 by
N. Vavilov. - Vavilov centers are regions where a high diversity of crop wild relatives can be found, representing the natural relatives of domesticated crop plants. Later in 1935 Vavilov divided the centers into
12, giving the following list:- Chinese center
- Indian center
- Indo-Malayan center
- Central Asiatic center
- Persian center
- Mediterranean center
- Abyssinian center
- North American center
- South American center
- Central American center
- Chilean center
- Brazilian-Paraguayan center
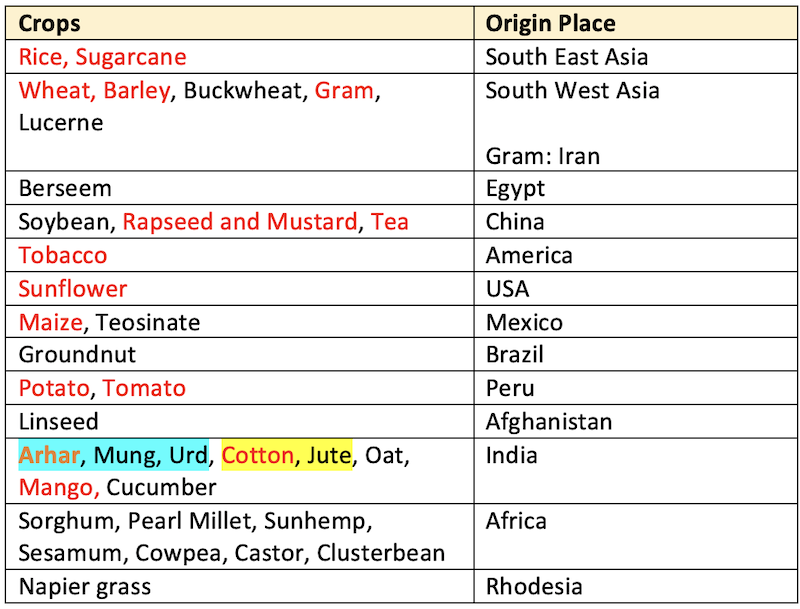
Origin Places of Important Crops
Law of homologous series
- The concept of parallel variation also known as law of homologous series of variation was developed by
Vavilov (1951)based on his study of crop diversity and centres of origin. - Law of homologous series states that a particular variation observed in a crop species is also expected to be available in its related species.
- For instance, if we get dwarf collections in one species of a crop, the same may be observed in another related species also.
- Vavilov used principle of homologous series of variation as a clue for discovering similar characters in related species.
- A center of origin (or center of diversity) is a geographical area where a group of organisms, either domesticated or wild, first developed its distinctive properties.
- They are also considered
centers of diversity. - Centers of origin were first identified in 1924 by
N. Vavilov. - Vavilov centers are regions where a high diversity of crop wild relatives can be found, representing the natural relatives of domesticated crop plants. Later in 1935 Vavilov divided the centers into
12, giving the following list:- Chinese center
- Indian center
- Indo-Malayan center
- Central Asiatic center
- Persian center
- Mediterranean center
- Abyssinian center
- North American center
- South American center
- Central American center
- Chilean center
- Brazilian-Paraguayan center
Origin Places of Important Crops

Law of …
Become Successful With AgriDots
Learn the essential skills for getting a seat in the Exam with
🦄 You are a pro member!
Only use this page if purchasing a gift or enterprise account
Plan
Rs
- Unlimited access to PRO courses
- Quizzes with hand-picked meme prizes
- Invite to private Discord chat
- Free Sticker emailed
Lifetime
Rs
1,499
once
- All PRO-tier benefits
- Single payment, lifetime access
- 4,200 bonus xp points
- Next Level
T-shirt shipped worldwide

Yo! You just found a 20% discount using 👉 EASTEREGG

High-quality fitted cotton shirt produced by Next Level Apparel